Production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis MZ-7 grown on pharmamedia commercial medium
- PMID: 17550616
- PMCID: PMC1894814
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-6-17
Production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis MZ-7 grown on pharmamedia commercial medium
Abstract
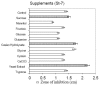
Background: Commercial medium (Pharmamedia) was investigated for the production of surfactin by Bacillus subtilis MZ-7. Different media (defined, semi-defined, and complex media) were compared for the production of surfactin after fixing the least influential variables in standardized fermentation conditions. Carbohydrate and nitrogen supplements were also tried to improve production in Pharmamedia.
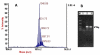
Results: Surfactin production was confirmed using PCR along with other analytical techniques and monitored by RP-HPLC and MALDI-TOF-MS. We found that optimized and brain heart infusion media were best for production of surfactin (280 mg/L) and a relatively comparable production with Pharmamedia (220 mg/L), however, supplementing Pharmamedia with Fe+ (4.0 mM) and sucrose (2 g/L) leads to a maximum production of about (300 mg/L).
Conclusion: Cottonseed-derived medium proved to be a suitable substrate for the production of bioactive substances including surfactin, a useful compound in both medical and biotechnological fields. The medium provided not only higher product accumulations but at considerably lower cost with potential for large scale industrial applications.
Figures

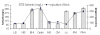
References
-
- Hosono K, Suzuki H. Acylpeptides, the inhibitors of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. I. Purification, physicochemical properties and structures of fatty acid residues. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983;36:667–673. - PubMed
-
- Kakinuma A, Hori M, Isono M, Tamura G, Arima K. Determination of amino acid sequence in surfactin, a crystalline peptide lipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis . Agric Biol Chem. 1969;33:971–972.
-
- Vanittanakom N, Loeffler W, Koch U, Jung G. Fengycin-a novel antifungal lipopeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis F-29-3. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986;39:888–901. - PubMed
-
- Besson F, Peypoux F, Michel G, Delcambe L. Identification of antibiotics of iturin group in various strains of Bacillus subtilis . J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978;31:284–288. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

