Identification of the circadian transcriptome in adult mouse skeletal muscle
- PMID: 17550994
- PMCID: PMC6080860
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00066.2007
Identification of the circadian transcriptome in adult mouse skeletal muscle
Abstract
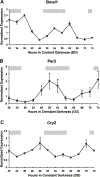
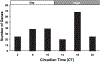
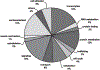
Circadian rhythms are approximate 24-h behavioral and physiological cycles that function to prepare an organism for daily environmental changes. The basic clock mechanism is a network of transcriptional-translational feedback loops that drive rhythmic expression of genes over a 24-h period. The objectives of this study were to identify transcripts with a circadian pattern of expression in adult skeletal muscle and to determine the effect of the Clock mutation on gene expression. Expression profiling on muscle samples collected every 4 h for 48 h was performed. Using COSOPT, we identified a total of 215 transcripts as having a circadian pattern of expression. Real-time PCR results verified the circadian expression of the core clock genes, Bmal1, Per2, and Cry2. Annotation revealed cycling genes were involved in a range of biological processes including transcription, lipid metabolism, protein degradation, ion transport, and vesicular trafficking. The tissue specificity of the skeletal muscle circadian transcriptome was highlighted by the presence of known muscle-specific genes such as Myod1, Ucp3, Atrogin1 (Fbxo32), and Myh1 (myosin heavy chain IIX). Expression profiling was also performed on muscle from the Clock mutant mouse and sarcomeric genes such as actin and titin, and many mitochondrial genes were significantly downregulated in the muscle of Clock mutant mice. Defining the circadian transcriptome in adult skeletal muscle and identifying the significant alterations in gene expression that occur in muscle of the Clock mutant mouse provide the basis for understanding the role of circadian rhythms in the daily maintenance of skeletal muscle.
Figures
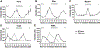
References
-
- Akashi M, Takumi T. The orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha regulates circadian transcription of the mammalian core-clock Bmal1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 441–448, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Akhtar RA, Reddy AB, Maywood ES, Clayton JD, King VM, Smith AG, Gant TW, Hastings MH, Kyriacou CP. Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Curr Biol 12: 540–550, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RA, Joyce C, Davis M, Reagan JW, Clark M, Shelness GS, Rudel LL. Identification of a form of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase specific to liver and intestine in nonhuman primates. J Biol Chem 273: 26747–26754, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Beatham J, Romero R, Townsend SK, Hacker T, van der Ven PF, Blanco G. Filamin C interacts with the muscular dystrophy KY protein and is abnormally distributed in mouse KY deficient muscle fibres. Hum Mol Genet 13: 2863–2874, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

