Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: clinical features, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment
- PMID: 17551069
- PMCID: PMC2600052
- DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.2006.054759
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: clinical features, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment
Abstract
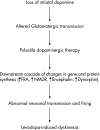
Levodopa is the most effective drug for treating Parkinson's disease. However, long-term use of levodopa is often complicated by significantly disabling fluctuations and dyskinesias negating its beneficial effects. Younger age of Parkinson's disease onset, disease severity, and high levodopa dose increase the risk of development of levodopa-induced dyskinesias (LID). The underlying mechanisms for LID are unclear though recent studies indicate the importance of pulsatile stimulation of striatal postsynaptic receptors in their pathogenesis. The non-human primates with MPTP-induced parkinsonism serve as a useful model to study dyskinesia. Once established, LID are difficult to treat and therefore efforts should be made to prevent them. The therapeutic and preventative strategies for LID include using a lower dosage of levodopa, employing dopamine agonists as initial therapy in Parkinson's disease, amantadine, atypical neuroleptics, and neurosurgery. LID can adversely affect the quality of life and increase the cost of healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared
References
-
- Cotzias G C, Papavasiliou P S, Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism – chronic treatment with L‐dopa. N Engl J Med 1969280337–345. - PubMed
-
- Duvoisin R C. Hyperkinetic responses with L‐DOPA. In: Yahr MD, ed. Current concepts in the treatment of parkinsonism. New York: Raven Press, 1974203–210.
-
- Parkinson's Study Group Impact of deprenyl and tocopherol treatment on Parkinson's disease in DATATOP patients requiring levodopa. Parkinson Study Group. Ann Neurol 19963937–45. - PubMed
-
- Kumar N, Van Gerpen J A, Bower J H.et al Levodopa‐dyskinesia incidence by age of Parkinson's disease onset. Mov Disord 200520342–344. - PubMed
-
- Sossi V, de la Fuente‐Fernandez R, Schulzer M.et al Age‐related differences in levodopa dynamics in Parkinson's: implications for motor complications. Brain 2006129(Pt 4)1050–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical