Effect of serum creatine kinase-MBmass on the early and hierarchical diagnosis of related artery reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction
- PMID: 17551076
- PMCID: PMC2600043
- DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.2006.056796
Effect of serum creatine kinase-MBmass on the early and hierarchical diagnosis of related artery reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate creatine kinase-MBmass (CK-MBmass) for the early diagnosis of infarct-related artery (IRA) patency after thrombolysis and the hierarchical diagnosis of related artery reperfusion (RAR).
Patients and methods: CK-MBmass and creatine kinase-MBactivity (CK-MBactivity) were measured kinetically in 48 patients treated with thrombolysis and 96 patients treated with routine drugs.
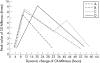
Results: In the continuous-RAR (CRAR) group, the peak values of CK-MBmass and CK-MBactivity appeared at < or =12 h, the peak durations were maintained for < or =8 h before decreasing to normal at < or =42 h, which occurred more quickly than those values in the non-RAR (NRAR) group. In the temporary-RAR (TRAR) group, the peak values appeared at < or =12 h, but no significant differences were found between the TRAR and NRAR groups in the time that the peak durations lasted before decreasing to normal values. In the reobliteration group after RAR, the peak values appeared at < or =12 h, and the peak durations were maintained for < or =8 h. After returning to the normal, a second peak appeared, and the time required for the values to return to normal was prolonged significantly.
Conclusions: CK-MBmass could be used as an indicator of RAR after thrombolysis; and the kinetic changes of serum CK-MBmass could be used for the hierarchical diagnosis of RAR in acute myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared.
References
-
- Takagi Y, Yasuhara T, Gomi K. Creatine kinase and its isozymes. Rinsho Byori 200111652–61. - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E, Antman E M, Beasley J W.et al ACC/AHA guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina and non‐ST‐segment elevation myocardial infarction. A report of the American College of Cardiology/AmericanHeart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Committee on the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina). J Am Coll Cardiol 200036970–1062. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials