Tandem repeat analysis for surveillance of human Salmonella Typhimurium infections
- PMID: 17552091
- PMCID: PMC2725892
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1303.060460
Tandem repeat analysis for surveillance of human Salmonella Typhimurium infections
Abstract
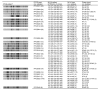
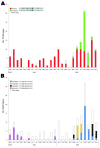
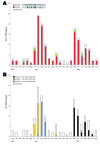
In Denmark, as part of the national laboratory-based surveillance system of human enteric infections, all Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium isolates are currently subtyped by using phage typing, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). We evaluated the value of real-time typing that uses multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeats analysis (MLVA) of S. Typhimurium to detect possible outbreaks. Because only a few subtypes identified by PFGE and phage typing account for most infections, we included MLVA typing in the routine surveillance in a 2-year period beginning December 2003. The 1,019 typed isolates were separated into 148 PFGE types and 373 MLVA types. Several possible outbreaks were detected and confirmed. MLVA was particularly valuable for discriminating within the most common phage types. MLVA was superior to PFGE for both surveillance and outbreak investigations of S. Typhimurium.
Figures
References
-
- Annual report on zoonoses in Denmark 2004. Copenhagen: Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries; 2005.
-
- Struelens MJ. Consensus guidelines for appropriate use and evaluation of microbial epidemiologic typing systems. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1996;2:2–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
