Neural correlates of mapping from phonology to orthography in children performing an auditory spelling task
- PMID: 17552934
- PMCID: PMC2638504
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00598.x
Neural correlates of mapping from phonology to orthography in children performing an auditory spelling task
Abstract
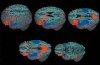
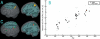
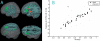
Age-related differences (9- to 15-year-olds) in the neural correlates of mapping from phonology to orthography were examined with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Participants were asked to determine if two spoken words had the same spelling for the rime (corresponding letters after the first consonant or consonant cluster). Some of the word pairs had conflicting orthography and phonology (e.g. jazz-has, pint-mint) whereas other pairs had non-conflicting information (e.g. press-list, gate-hate) (see Table 1). There were age-related increases in activation for lexical processing (across conflicting and non-conflicting conditions) in left inferior parietal lobule, suggesting that older children have a more elaborated system for mapping between phonology and orthography that includes connections at different grain sizes (e.g. phonemes, onset-rimes, syllables). In addition, we found that the conflicting conditions had lower accuracy, slower reaction time and greater activation in left inferior frontal gyrus as compared to non-conflicting conditions. Higher accuracy was also correlated with greater activation in left inferior frontal gyrus for the most difficult conflicting condition (e.g. jazz-has). The finding of both a conflict effect and a correlation with accuracy in left inferior frontal gyrus suggests that this region may be involved in resolving the conflict between orthographic and phonological representations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deficient orthographic and phonological representations in children with dyslexia revealed by brain activation patterns.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2006 Oct;47(10):1041-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01684.x. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2006. PMID: 17073983 Free PMC article.
-
Effective brain connectivity in children with reading difficulties during phonological processing.Brain Lang. 2008 Nov;107(2):91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2007.12.009. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Brain Lang. 2008. PMID: 18226833 Free PMC article.
-
Neural correlates of priming effects in children during spoken word processing with orthographic demands.Brain Lang. 2010 Aug;114(2):80-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Aug 8. Brain Lang. 2010. PMID: 19665784 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental increase in top-down and bottom-up processing in a phonological task: an effective connectivity, fMRI study.J Cogn Neurosci. 2009 Jun;21(6):1135-45. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2009.21065. J Cogn Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 18702576 Free PMC article.
-
Reading acquisition reorganizes the phonological awareness network only in alphabetic writing systems.Hum Brain Mapp. 2013 Dec;34(12):3354-68. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22147. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Hum Brain Mapp. 2013. PMID: 22815229 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cultural constraints on brain development: evidence from a developmental study of visual word processing in mandarin chinese.Cereb Cortex. 2010 May;20(5):1223-33. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp186. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 19773547 Free PMC article.
-
Reading disability is characterized by reduced print-speech convergence.Child Dev. 2024 Nov-Dec;95(6):1982-1999. doi: 10.1111/cdev.14134. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Child Dev. 2024. PMID: 39032033 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental changes in the inferior frontal cortex for selecting semantic representations.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2011 Jul;1(3):338-50. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2011.01.005. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22337757 Free PMC article.
-
Reading in the brain of children and adults: a meta-analysis of 40 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 May;36(5):1963-81. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22749. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015. PMID: 25628041 Free PMC article.
-
Children With Reading Difficulty Rely on Unimodal Neural Processing for Phonemic Awareness.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Nov 14;13:390. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00390. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31798430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baayen RH, Piepenbrock R, Gulikers L. The celex lexical database (Version Release 2) [CD-ROM] Linguistic Data Consortium, University of Pennsylvania; Philadelphia, PA: 1995.
-
- Berninger VW, Abbott RD, Jones J, Gould L, Anderson-Youngstrom M, Wolf BJ, Apel K. Early development of language by hand: composing, reading, listening, and speaking connections; three letter-writing modes; and fast mapping in spelling. Developmental Neuropsychology. 2006;29(1):61–92. - PubMed
-
- Booth JR, Burman DD, Meyer JR, Gitelman DR, Parrish TR, Mesulam MM. Functional anatomy of intra- and cross-modal lexical tasks. NeuroImage. 2002;16:7–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

