Bluetongue in Belgium, 2006
- PMID: 17553280
- PMCID: PMC2725968
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1304.061136
Bluetongue in Belgium, 2006
Abstract
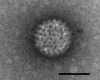
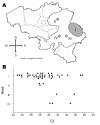
Bluetongue has emerged recently in Belgium. A bluetongue virus strain was isolated and characterized as serotype 8. Two new real-time reverse transcription-quantitative PCRs (RT-qPCRs) that amplified 2 different segments of bluetongue virus detected this exotic strain. These 2 RT-qPCRs detected infection earlier than a competitive ELISA for antibody detection.
Figures
References
-
- Tabachnick WJ. Culicoides and the global epidemiology of bluetongue virus infection. Vet Ital. 2004;40:145–50. - PubMed
-
- OIE Animal Health Department. Bluetongue – Netherlands, Belgium, Germany-OIE. ProMed. August 21, 2006. Accessed at http://www.promedmail.org, archive no.: 20060821.2353.
-
- Communication Directorate General. Bluetongue confirmed in France. EU Midday-express. [cited 2006 Aug 31]. Available from http://europa.eu.int/rapid, reference: MEX/06/0831
-
- Toussaint JF, Sailleau C, Breard E, Zientara S, de Clercq K. Bluetongue virus detection by two real-time RT-qPCRs targeting two different genomic segments. J. Virol. Methods. 2006; [Epub ahead of print]. PMID: 17196266 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
