Functional genetic selection of Helix 66 in Escherichia coli 23S rRNA identified the eukaryotic-binding sequence for ribosomal protein L2
- PMID: 17553838
- PMCID: PMC1919495
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm356
Functional genetic selection of Helix 66 in Escherichia coli 23S rRNA identified the eukaryotic-binding sequence for ribosomal protein L2
Abstract
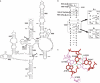
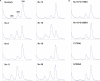
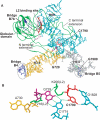
Ribosomal protein L2 is a highly conserved primary 23S rRNA-binding protein. L2 specifically recognizes the internal bulge sequence in Helix 66 (H66) of 23S rRNA and is localized to the intersubunit space through formation of bridge B7b with 16S rRNA. The L2-binding site in H66 is highly conserved in prokaryotic ribosomes, whereas the corresponding site in eukaryotic ribosomes has evolved into distinct classes of sequences. We performed a systematic genetic selection of randomized rRNA sequences in Escherichia coli, and isolated 20 functional variants of the L2-binding site. The isolated variants consisted of eukaryotic sequences, in addition to prokaryotic sequences. These results suggest that L2/L8e does not recognize a specific base sequence of H66, but rather a characteristic architecture of H66. The growth phenotype of the isolated variants correlated well with their ability of subunit association. Upon continuous cultivation of a deleterious variant, we isolated two spontaneous mutations within domain IV of 23S rRNA that compensated for its weak subunit association, and alleviated its growth defect, implying that functional interactions between intersubunit bridges compensate ribosomal function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The 3D arrangement of the 23 S and 5 S rRNA in the Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal subunit based on a cryo-electron microscopic reconstruction at 7.5 A resolution.J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 21;298(1):35-59. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3635. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10756104
-
Selecting rRNA binding sites for the ribosomal proteins L4 and L6 from randomly fragmented rRNA: application of a method called SERF.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Apr 25;97(9):4597-602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.090009297. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10781065 Free PMC article.
-
The 23 S rRNA environment of ribosomal protein L9 in the 50 S ribosomal subunit.J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 14;297(5):1129-43. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3621. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10764578
-
Mutational analysis of 23S ribosomal RNA structure and function in Escherichia coli.Adv Genet. 1999;41:157-95. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60153-4. Adv Genet. 1999. PMID: 10494619 Review. No abstract available.
-
RNA-protein interactions in the Escherichia coli ribosome.Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):927-36. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90134-m. Biochimie. 1991. PMID: 1720671 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a novel methyltransferase, Bmt2, responsible for the N-1-methyl-adenosine base modification of 25S rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 May 1;41(10):5428-43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt195. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23558746 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting bacterial phylogeny: Natural and experimental evidence for horizontal gene transfer of 16S rRNA.Mob Genet Elements. 2013 Jan 1;3(1):e24210. doi: 10.4161/mge.24210. Mob Genet Elements. 2013. PMID: 23734299 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational robustness of 16S ribosomal RNA, shown by experimental horizontal gene transfer in Escherichia coli.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 20;109(47):19220-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213609109. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23112186 Free PMC article.
-
Bactobolin resistance is conferred by mutations in the L2 ribosomal protein.mBio. 2012 Dec 18;3(6):e00499-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00499-12. mBio. 2012. PMID: 23249812 Free PMC article.
-
Selection for intragenic suppressors of lethal 23S rRNA mutations in Escherichia coli identifies residues important for ribosome assembly and function.Mol Genet Genomics. 2007 Dec;278(6):677-87. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0284-3. Epub 2007 Sep 6. Mol Genet Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17828421
References
-
- Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Moore PB, Steitz TA. The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science. 2000;289:905–920. - PubMed
-
- Harms J, Schluenzen F, Zarivach R, Bashan A, Gat S, Agmon I, Bartels H, Franceschi F, Yonath A. High resolution structure of the large ribosomal subunit from a mesophilic eubacterium. Cell. 2001;107:679–688. - PubMed
-
- Wimberly BT, Brodersen DE, Clemons WM, Jr, Morgan-Warren RJ, Carter AP, Vonrhein C, Hartsch T, Ramakrishnan V. Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature. 2000;407:327–339. - PubMed
-
- Schluenzen F, Tocilj A, Zarivach R, Harms J, Gluehmann M, Janell D, Bashan A, Bartels H, Agmon I, et al. Structure of functionally activated small ribosomal subunit at 3.3 angstroms resolution. Cell. 2000;102:615–623. - PubMed
-
- Schuwirth BS, Borovinskaya MA, Hau CW, Zhang W, Vila-Sanjurjo A, Holton JM, Cate JH. Structures of the bacterial ribosome at 3.5 Å resolution. Science. 2005;310:827–834. - PubMed

