iPDA: integrated protein disorder analyzer
- PMID: 17553839
- PMCID: PMC1933224
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm353
iPDA: integrated protein disorder analyzer
Abstract
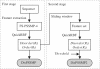
This article presents a web server iPDA, which aims at identifying the disordered regions of a query protein. Automatic prediction of disordered regions from protein sequences is an important problem in the study of structural biology. The proposed classifier DisPSSMP2 is different from several existing disorder predictors by its employment of position-specific scoring matrices with respect to physicochemical properties (PSSMP), where the physicochemical properties adopted here especially take the disorder propensity of amino acids into account. The web server iPDA integrates DisPSSMP2 with several other sequence predictors in order to investigate the functional role of the detected disordered region. The predicted information includes sequence conservation, secondary structure, sequence complexity and hydrophobic clusters. According to the proportion of the secondary structure elements predicted, iPDA dynamically adjusts the cutting threshold of determining protein disorder. Furthermore, a pattern mining package for detecting sequence conservation is embedded in iPDA for discovering potential binding regions of the query protein, which is really helpful to uncovering the relationship between protein function and its primary sequence. The web service is available at http://biominer.bime.ntu.edu.tw/ipda and mirrored at http://biominer.cse.yzu.edu.tw/ipda.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PROMALS web server for accurate multiple protein sequence alignments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W649-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm227. Epub 2007 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17452345 Free PMC article.
-
PrDOS: prediction of disordered protein regions from amino acid sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W460-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm363. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17567614 Free PMC article.
-
DOMAC: an accurate, hybrid protein domain prediction server.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W354-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm390. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17553833 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating protein secondary structure prediction and multiple sequence alignment.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2004 Aug;5(4):249-66. doi: 10.2174/1389203043379675. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2004. PMID: 15320732 Review.
-
[From sequence variability to structural and functional prediction: modeling of homologous protein families].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(3):239-244. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017030. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 29412135 Review. French.
Cited by
-
DisPredict: A Predictor of Disordered Protein Using Optimized RBF Kernel.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 30;10(10):e0141551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141551. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26517719 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of Pyrococcus furiosus RPP21, a component of the archaeal RNase P holoenzyme, and interactions with its RPP29 protein partner.Biochemistry. 2008 Nov 11;47(45):11704-10. doi: 10.1021/bi8015982. Epub 2008 Oct 16. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18922021 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting RNA-binding residues from evolutionary information and sequence conservation.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 2;11 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S4-S2. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143803 Free PMC article.
-
Disorder-to-order conformational transitions in protein structure and its relationship to disease.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Oct;330(1-2):105-20. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0105-6. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19357935 Review.
-
An Overview of Predictors for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins over 2010-2014.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 29;16(10):23446-62. doi: 10.3390/ijms161023446. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26426014 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wright PE, Dyson HJ. Intrinsically unstructured proteins: re-assessing the protein structure-function paradigm. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;293:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Fink AL. Natively unfolded proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005;15:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Jones DT, Ward JJ. Prediction of disordered regions in proteins from position specific score matrices. Proteins. 2003;53(Suppl. 6):573–578. - PubMed
-
- Dunker AK, Garner E, Guilliot S, Romero P, Albrecht K, Hart J, Obradovic Z, Kissinger C, Villafranca JE. Protein disorder and the evolution of molecular recognition: theory, predictions and observations. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 1998:473–484. - PubMed
-
- Romero P, Obradovic Z, Dunker AK. Sequence data analysis for long disordered regions prediction in the Calcineurin family. Genome Inform Ser. Workshop Genome Inform. 1997;8:110–124. - PubMed

