Vpr cytopathicity independent of G2/M cell cycle arrest in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 17553871
- PMCID: PMC1951439
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00122-07
Vpr cytopathicity independent of G2/M cell cycle arrest in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected CD4+ T cells
Abstract
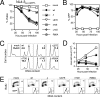
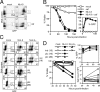
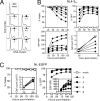
The mechanism of CD4(+) T-cell depletion in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected individuals remains unknown, although mounting evidence suggests that direct viral cytopathicity contributes to this loss. The HIV-1 Vpr accessory protein causes cell death and arrests cells in the G(2)/M phase; however, the molecular mechanism underlying these properties is not clear. Mutation of hydrophobic residues on the surface of its third alpha-helix disrupted Vpr toxicity, G(2)/M arrest induction, nuclear localization, and self-association, implicating this region in multiple Vpr functions. Cytopathicity by virion-delivered mutant Vpr protein correlated with G(2)/M arrest induction but not nuclear localization or self-association. However, infection with whole virus encoding these Vpr mutants did not abrogate HIV-1-induced cell killing. Rather, mutant Vpr proteins that are impaired for G(2)/M block still prevented infected cell proliferation, and this property correlated with the death of infected cells. Chemical agents that inhibit infected cells from entering G(2)/M also did not reduce HIV-1 cytopathicity. Combined, these data implicate Vpr in HIV-1 killing through a mechanism involving inhibiting cell division but not necessarily in G(2)/M. Thus, the hydrophobic region of the third alpha-helix of Vpr is crucial for mediating G(2)/M arrest, nuclear localization, and self-association but dispensable for HIV-1 cytopathicity due to residual cell proliferation blockade mediated by a separate region of the protein.
Figures
References
-
- Agostini, I., J. M. Navarro, F. Rey, M. Bouhamdan, B. Spire, R. Vigne, and J. Sire. 1996. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr transactivator: cooperation with promoter-bound activator domains and binding to TFIIB. J. Mol. Biol. 261:599-606. - PubMed
-
- Azuma, A., A. Matsuo, T. Suzuki, T. Kurosawa, X. Zhang, and Y. Aida. 2006. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr induces cell cycle arrest at the G1 phase and apoptosis via disruption of mitochondrial function in rodent cells. Microbes Infect. 8:670-679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

