Expression of the mu opioid receptor in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transgenic rat model
- PMID: 17553897
- PMCID: PMC1951376
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00155-07
Expression of the mu opioid receptor in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transgenic rat model
Abstract
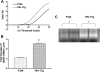
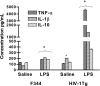
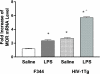
Opioids, via the mu opioid receptor (MOR), can exacerbate bacterial infections and the immunopathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection. Recently, an HIV-1 transgenic (HIV-1Tg) rat model containing circulating HIV-1 gp120 was created. Using real-time reverse transcription-PCR, we found that MOR mRNA levels were significantly higher in the peritoneal macrophages of the HIV-1Tg rat than those in control animals. Lipopolysaccharide, a bacterial endotoxin, induced secretion of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-beta (IL-beta), and IL-10 in the HIV-1Tg rat and further increased MOR expression. Ex vivo studies showed that MOR expression was up-regulated in the peritoneal macrophages of F344 control rats by exposure to serum from HIV-1Tg rats and that MOR up-regulation was abolished by addition of gp120 antibody to the serum. In human TPA-differentiated HL-60 cells, which are macrophage-like cells, LPS-induced MOR mRNA up-regulation was greater in gp120-pretreated cells than in vehicle-pretreated cells. Our data suggest that in individuals infected with HIV-1, the MOR is up-regulated, possibly by circulating HIV-1 proteins such as gp120, and HIV-1 proteins may play a significant role in modulating the response to bacterial infection in opioid-using HIV-infected individuals. Furthermore, our results demonstrate that the new HIV-1Tg rat model can be a valuable tool with which to study MOR gene expression and its effects in the continuous presence of HIV viral proteins.
Figures
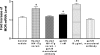

Similar articles
-
HIV-1 gp120 up-regulation of the mu opioid receptor in TPA-differentiated HL-60 cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Sep;6(9):1459-67. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.04.018. Epub 2006 May 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16846840
-
Modulation of OPRM1 Alternative Splicing by Morphine and HIV-1 Nef.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;17(1-2):277-288. doi: 10.1007/s11481-021-10009-4. Epub 2021 Aug 21. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34420144 Free PMC article.
-
A vitamin A deficient diet enhances proinflammatory cytokine, Mu opioid receptor, and HIV-1 expression in the HIV-1 transgenic rat.J Neuroimmunol. 2007 Apr;185(1-2):29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Feb 7. J Neuroimmunol. 2007. PMID: 17289162 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid μ-receptors as new target for insulin resistance.Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Sep;139(3):334-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 18. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23688574 Review.
-
Behavioral and molecular evidence for a feedback interaction between morphine and HIV-1 viral proteins.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;7(2):332-40. doi: 10.1007/s11481-011-9324-1. Epub 2011 Nov 15. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22083500 Review.
Cited by
-
The synthetic opioid fentanyl enhances viral replication in vitro.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 14;16(4):e0249581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249581. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33852610 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 (SOCS-1): A mechanism for dysregulated T helper-1 responses in HIV-1 disease.Virology. 2009 Mar 1;385(1):126-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.11.039. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19135225 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in the HIV-1 transgenic rat.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 4;9:3. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22216977 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of TRPM7 in Alcohol-Induced Damage of the Blood-Brain Barrier in the Presence of HIV Viral Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1910. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031910. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768230 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific actions of HIV-Tat and morphine on opioid receptor expression in glia.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Jul;86(9):2100-10. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21653. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18338799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbaro, G., A. Scozzafava, A. Mastrolorenzo, and C. T. Supuran. 2005. Highly active antiretroviral therapy: current state of the art, new agents and their pharmacological interactions useful for improving therapeutic outcome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11:1805-1843. - PubMed
-
- Beck, M., A. Mirmohammadsadegh, B. Franz, J. Blanke, and U. R. Hengge. 2002. Opioid receptors on white blood cells: effect of HIV infection and methadone treatment. Pain 98:187-194. - PubMed
-
- Beltran, J. A., A. Pallur, and S. L. Chang. 2006. HIV-1 gp120 up-regulation of the mu opioid receptor in TPA-differentiated HL-60 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 6:1459-1467. - PubMed
-
- Beltran, J. A., J. Peek, and S. L. Chang. 2006. Expression and regulation of the mu opioid peptide receptor in TPA-differentiated HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 6:1331-1340. - PubMed
-
- Bestilny, L. J., and K. T. Riabowol. 2000. A role for serine proteases in mediating phorbol ester-induced differentiation of HL-60 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 256:264-271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

