Parkin-mediated monoubiquitination of the PDZ protein PICK1 regulates the activity of acid-sensing ion channels
- PMID: 17553932
- PMCID: PMC1949385
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-11-1027
Parkin-mediated monoubiquitination of the PDZ protein PICK1 regulates the activity of acid-sensing ion channels
Abstract
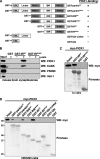
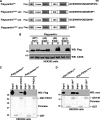
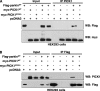
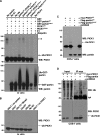
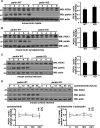
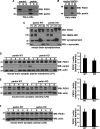
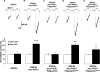
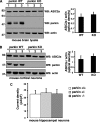
Mutations in the parkin gene result in an autosomal recessive juvenile-onset form of Parkinson's disease. As an E3 ubiquitin-ligase, parkin promotes the attachment of ubiquitin onto specific substrate proteins. Defects in the ubiquitination of parkin substrates are therefore believed to lead to neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. Here, we identify the PSD-95/Discs-large/Zona Occludens-1 (PDZ) protein PICK1 as a novel parkin substrate. We find that parkin binds PICK1 via a PDZ-mediated interaction, which predominantly promotes PICK1 monoubiquitination rather than polyubiquitination. Consistent with monoubiquitination and recent work implicating parkin in proteasome-independent pathways, parkin does not promote PICK1 degradation. However, parkin regulates the effects of PICK1 on one of its other PDZ partners, the acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC). Overexpression of wild-type, but not PDZ binding- or E3 ubiquitin-ligase-defective parkin abolishes the previously described, protein kinase C-induced, PICK1-dependent potentiation of ASIC2a currents in non-neuronal cells. Conversely, the loss of parkin in hippocampal neurons from parkin knockout mice unmasks prominent potentiation of native ASIC currents, which is normally suppressed by endogenous parkin in wild-type neurons. Given that ASIC channels contribute to excitotoxicity, our work provides a mechanism explaining how defects in parkin-mediated PICK1 monoubiquitination could enhance ASIC activity and thereby promote neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of the synaptic protein PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase 1) with the non-voltage gated sodium channels BNC1 (brain Na+ channel 1) and ASIC (acid-sensing ion channel).Biochem J. 2002 Feb 1;361(Pt 3):443-50. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3610443. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 11802773 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase C stimulates the acid-sensing ion channel ASIC2a via the PDZ domain-containing protein PICK1.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 27;277(52):50463-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M208848200. Epub 2002 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12399460
-
PICK1 regulates the trafficking of ASIC1a and acidotoxicity in a BAR domain lipid binding-dependent manner.Mol Brain. 2010 Dec 21;3:39. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-3-39. Mol Brain. 2010. PMID: 21176140 Free PMC article.
-
Activation mechanisms of the E3 ubiquitin ligase parkin.Biochem J. 2017 Aug 30;474(18):3075-3086. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170476. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 28860335 Review.
-
Linking F-box protein 7 and parkin to neuronal degeneration in Parkinson's disease (PD).Mol Brain. 2016 Apr 18;9:41. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0218-2. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27090516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parkin Inhibits Static Mechanical Pain by Suppressing Membrane Trafficking of Mechano-transducing Ion Channel TACAN.Neurosci Bull. 2022 Apr;38(4):429-434. doi: 10.1007/s12264-022-00843-8. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Neurosci Bull. 2022. PMID: 35353345 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protein S-nitrosylation and oxidation contribute to protein misfolding in neurodegeneration.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Aug 20;172:562-577. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.002. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34224817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggresome formation and neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(1):47-60. doi: 10.2174/092986708783330692. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18220762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review for the pharmacological effects of paeoniflorin in the nervous system.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 15;13:898955. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.898955. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36046834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2010;25 Suppl 1(0 1):S32-9. doi: 10.1002/mds.22798. Mov Disord. 2010. PMID: 20187240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Askwith C. C., Wemmie J. A., Price M. P., Rokhlina T., Welsh M. J. Acid-sensing ion channel 2 (ASIC2) modulates ASIC1 H+-activated currents in hippocampal neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:18296–18305. - PubMed
-
- Baron A., Deval E., Salinas M., Lingueglia E., Voilley N., Lazdunski M. Protein kinase C stimulates the acid-sensing ion channel ASIC2a via the PDZ domain-containing protein PICK1. J. Biol. Chem. 2002a;277:50463–50468. - PubMed
-
- Chung K. K., Zhang Y., Lim K. L., Tanaka Y., Huang H., Gao J., Ross C. A., Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M. Parkin ubiquitinates the alpha-synuclein-interacting protein, synphilin-1, implications for Lewy-body formation in Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 2001;7:1144–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

