Amyloid deposition begins in the striatum of presenilin-1 mutation carriers from two unrelated pedigrees
- PMID: 17553989
- PMCID: PMC3265970
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0730-07.2007
Amyloid deposition begins in the striatum of presenilin-1 mutation carriers from two unrelated pedigrees
Abstract
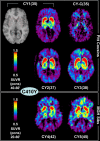
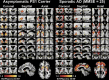
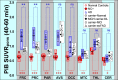
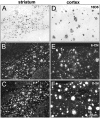
The amyloid cascade hypothesis suggests that the aggregation and deposition of amyloid-beta protein is an initiating event in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Using amyloid imaging technology, such as the positron emission tomography (PET) agent Pittsburgh compound-B (PiB), it is possible to explore the natural history of preclinical amyloid deposition in people at high risk for AD. With this goal in mind, asymptomatic (n = 5) and symptomatic (n = 5) carriers of presenilin-1 (PS1) mutations (C410Y or A426P) that lead to early-onset AD and noncarrier controls from both kindreds (n = 2) were studied with PiB-PET imaging and compared with sporadic AD subjects (n = 12) and controls from the general population (n = 18). We found intense and focal PiB retention in the striatum of all 10 PS1 mutation carriers studied (ages 35-49 years). In most PS1 mutation carriers, there also were increases in PiB retention compared with controls in cortical brain areas, but these increases were not as great as those observed in sporadic AD subjects. The two PS1 mutation carriers with a clinical diagnosis of early-onset AD did not show the typical regional pattern of PiB retention observed in sporadic AD. Postmortem evaluation of tissue from two parents of PS1C410Y subjects in this study confirmed extensive striatal amyloid deposition, along with typical cortical deposition. The early, focal striatal amyloid deposition observed in these PS1 mutation carriers is often is not associated with clinical symptoms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High striatal amyloid beta-peptide deposition across different autosomal Alzheimer disease mutation types.Arch Neurol. 2009 Dec;66(12):1537-44. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2009.285. Arch Neurol. 2009. PMID: 20008660
-
Striatal amyloid is associated with tauopathy and memory decline in familial Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Feb 4;11(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0468-1. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30717814 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon-11-Pittsburgh compound B positron emission tomography imaging of amyloid deposition in presenilin 1 mutation carriers.Brain. 2011 Jan;134(Pt 1):293-300. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq310. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21084313
-
Association Between Amyloid and Tau Accumulation in Young Adults With Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer Disease.JAMA Neurol. 2018 May 1;75(5):548-556. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.4907. JAMA Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29435558 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the positron emission tomography tracer Pittsburgh compound-B reflects the amount of amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease brain but not in transgenic mouse brain.J Neurosci. 2005 Nov 16;25(46):10598-606. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2990-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16291932 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Florbetapir PET analysis of amyloid-β deposition in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease kindred: a cross-sectional study.Lancet Neurol. 2012 Dec;11(12):1057-65. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70227-2. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Lancet Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23137949 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease and the prospect of presymptomatic intervention.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33 Suppl 1(0 1):S405-16. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-129026. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 22695623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking Molecular Pathways and Large-Scale Computational Modeling to Assess Candidate Disease Mechanisms and Pharmacodynamics in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Comput Neurosci. 2019 Aug 13;13:54. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2019.00054. eCollection 2019. Front Comput Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31456676 Free PMC article.
-
Novel PSEN1 (P284S) Mutation Causes Alzheimer's Disease with Cerebellar Amyloid β-Protein Deposition.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022;19(7):523-529. doi: 10.2174/1567205019666220718151357. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022. PMID: 35850649 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker modelling of early molecular changes in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Diagn Ther. 2014 Apr;18(2):213-27. doi: 10.1007/s40291-013-0069-9. Mol Diagn Ther. 2014. PMID: 24281842 Review.
References
-
- Archer HA, Edison P, Brooks DJ, Barnes J, Frost C, Yeatman T, Fox NC, Rossor MN. Amyloid load and cerebral atrophy in Alzheimer's disease: an 11C-PIB positron emission tomography study. Ann Neurol. 2006;60:145–147. - PubMed
-
- Becker JT, Boller F, Saxton J, McGonigle-Gibson KL. Normal rates of forgetting of verbal and non-verbal material in Alzheimer's disease. Cortex. 1987;23:59–72. - PubMed
-
- Benton AL. Differential behavioral effects in frontal lobe disease. Neuropsychologia. 1968;6:53–60.
-
- Benton AL, Sivan AB, Hamsher KD, Varney NR, Spreen O. A clinical manual. Ed 2. New York: Oxford UP; 1994. Contributions to neuropsychological assessment.
-
- Beyreuther K, Dyrks T, Hilbich C, Monning U, Konig G, Multhaup G, Pollwein P, Masters CL. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and beta A4 amyloid in Alzheimer's disease and Down syndrome. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;379:159–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
