Deletion of apolipoprotein E receptor-2 in mice lowers brain selenium and causes severe neurological dysfunction and death when a low-selenium diet is fed
- PMID: 17553992
- PMCID: PMC6672153
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1153-07.2007
Deletion of apolipoprotein E receptor-2 in mice lowers brain selenium and causes severe neurological dysfunction and death when a low-selenium diet is fed
Abstract
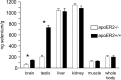
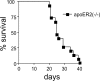
Selenoprotein P (Sepp1) is a plasma and extracellular protein that is rich in selenium. Deletion of Sepp1 results in sharp decreases of selenium levels in the brain and testis with dysfunction of those organs. Deletion of Sepp1 also causes increased urinary selenium excretion, leading to moderate depletion of whole-body selenium. The lipoprotein receptor apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (apoER2) binds Sepp1 and facilitates its uptake by Sertoli cells, thus providing selenium for spermatogenesis. Experiments were performed to assess the effect of apoER2 on the concentration and function of selenium in the brain and on whole-body selenium. ApoER2-/- and apoER2+/+ male mice were fed a semipurified diet with selenite added as the source of selenium. ApoER2-/- mice had depressed brain and testis selenium, but normal levels in liver, kidney, muscle, and the whole body. Feeding a selenium-deficient diet to apoER2-/- mice led to neurological dysfunction and death, with some of the characteristics exhibited by Sepp1-/- mice fed the same diet. Thus, although it does not affect whole-body selenium, apoER2 is necessary for maintenance of brain selenium and for prevention of neurological dysfunction and death under conditions of selenium deficiency, suggesting an interaction of apoER2 with Sepp1 in the brain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selenoprotein P and apolipoprotein E receptor-2 interact at the blood-brain barrier and also within the brain to maintain an essential selenium pool that protects against neurodegeneration.FASEB J. 2014 Aug;28(8):3579-88. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-252874. Epub 2014 Apr 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24760755 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (ApoER2) mediates selenium uptake from selenoprotein P by the mouse testis.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 20;282(16):12290-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611403200. Epub 2007 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17314095
-
Maternal-fetal transfer of selenium in the mouse.FASEB J. 2013 Aug;27(8):3249-56. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-231852. Epub 2013 May 7. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23651543 Free PMC article.
-
SeP, ApoER2 and megalin as necessary factors to maintain Se homeostasis in mammals.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012 Oct;26(4):262-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22683052 Review.
-
Selenoprotein P-expression, functions, and roles in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Nov;1790(11):1441-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.026. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19345254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selenoproteins and oxidative stress-induced inflammatory tumorigenesis in the gut.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Feb;74(4):607-616. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2339-2. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 27563706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenoprotein P expression in glioblastoma as a regulator of ferroptosis sensitivity: preservation of GPX4 via the cycling-selenium storage.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 5;14(1):682. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51259-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38182643 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations disrupting selenocysteine formation cause progressive cerebello-cerebral atrophy.Am J Hum Genet. 2010 Oct 8;87(4):538-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.09.007. Am J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20920667 Free PMC article.
-
From Selenium Absorption to Selenoprotein Degradation.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019 Nov;192(1):26-37. doi: 10.1007/s12011-019-01771-x. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019. PMID: 31222623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenoprotein P Regulates Synaptic Zinc and Reduces Tau Phosphorylation.Front Nutr. 2021 Jul 1;8:683154. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.683154. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34277682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beffert U, Weeber EJ, Durudas A, Qiu S, Masiulis I, Sweatt JD, Li WP, Adelmann G, Frotscher M, Hammer RE, Herz J. Modulation of synaptic plasticity and memory by Reelin involves differential splicing of the lipoprotein receptor Apoer2. Neuron. 2005;47:567–579. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Durudas A, Weeber EJ, Stolt PC, Giehl KM, Sweatt JD, Hammer RE, Herz J. Functional dissection of Reelin signaling by site-directed disruption of Disabled-1 adaptor binding to apolipoprotein E receptor 2: distinct roles in development and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci. 2006a;26:2041–2052. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Nematollah Farsian F, Masiulis I, Hammer RE, Yoon SO, Giehl KM, Herz J. ApoE receptor 2 controls neuronal survival in the adult brain. Curr Biol. 2006b;16:2446–2452. - PubMed
-
- Burk RF. Selenium (Se) and antioxidant mechanisms. Free Radical Res. 2006;40:S50.
-
- Burk RF, Lane JM. Modification of chemical toxicity by selenium deficiency. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1983;3:218–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
