A novel connection between rods and ON cone bipolar cells revealed by ectopic metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGluR7) in mGluR6-deficient mouse retinas
- PMID: 17553999
- PMCID: PMC6672139
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5646-06.2007
A novel connection between rods and ON cone bipolar cells revealed by ectopic metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGluR7) in mGluR6-deficient mouse retinas
Abstract
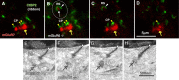
Since the discovery of direct chemical synapses between rod photoreceptor and OFF cone bipolar cells in mouse retinas, whether the ON cone bipolar cell also receive direct chemical input from rod has been a pending question. In finding that metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGluR7) was uniquely expressed in dendrites of ON cone bipolar cells in the mGluR6-deficient mouse retina, we used this ectopic mGluR7 immunoreactivity as a specific marker for the ON cone bipolar to search for its rod connection. Here, we show that a certain type of ON cone bipolar cell forms ribbon-associated synapses not only with cones, but also rods. This finding was verified in the wild-type mouse retina by three-dimensional reconstruction of bipolar cells from serial electron micrographs. These ON cone bipolars were further identified as corresponding to type 7 of mouse bipolar cell described by Ghosh et al. (2004) and also to the green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled type 7 bipolars in the alpha-gustducin-GFP transgenic mouse. Our findings suggest that, in mice, rod signals bifurcate into a third ON and OFF pathway in addition to the two known routes to cone bipolar cells: (1) via rod chemical synapse --> rod bipolar --> AII amacrine --> ON and OFF cone bipolar cells; (2) via rod-cone gap junction --> cone chemical synapse --> ON and OFF cone bipolar cells; and (3) via rod chemical synapse --> ON and OFF cone bipolar cells. This third novel pathway is thought to transmit fast and moderately light-sensitive rod signals, functioning to smooth out the intensity changes at the scotopic-mesopic interface.
Figures



References
-
- DeVries SH, Li W, Saszik S. Parallel processing in two transmitter microenvironments at the cone photoreceptor synapse. Neuron. 2006;50:735–748. - PubMed
-
- Dowling JE. Cambridge, MA: Harvard UP; 1987. The retina.
-
- Ghosh KK, Bujan S, Haverkamp S, Feigenspan A, Wässle H. Types of bipolar cells in the mouse retina. J Comp Neurol. 2004;469:70–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
