Neuron-specific inactivation of the hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha increases brain injury in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 17554006
- PMCID: PMC6672155
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0449-07.2007
Neuron-specific inactivation of the hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha increases brain injury in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia
Abstract
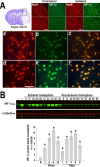
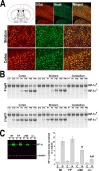
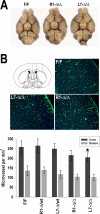
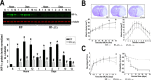
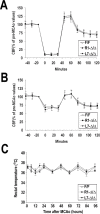
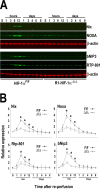
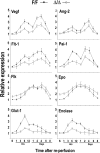
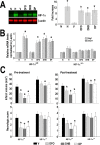
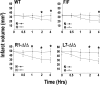
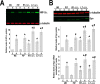
In the present study, we show a biphasic activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1) after stroke that lasts for up to 10 d, suggesting the involvement of the HIF pathway in several aspects of the pathophysiology of cerebral ischemia. We provide evidence that HIF-1-mediated responses have an overall beneficial role in the ischemic brain as indicated by increased tissue damage and reduced survival rate of mice with neuron-specific knockdown of HIF-1alpha that were subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. In addition, we demonstrated that drugs known to activate HIF-1 in cultured cells as well as in vivo had neuroprotective properties in this model of cerebral ischemia. This protective effect was significantly attenuated but not completely abolished in neuron-specific HIF-1alpha-deficient mice, suggesting that alternative mechanisms of neuroprotection are also implicated. Last, our study showed that hypoxia-induced tolerance to ischemia was preserved in neuron-specific HIF-1alpha-deficient mice, indicating that the neuroprotective effects of hypoxic preconditioning do not depend on neuronal HIF-1 activation.
Figures
References
-
- Althaus J, Bernaudin M, Petit E, Toutain J, Touzani O, Rami A. Expression of the gene encoding the pro-apoptotic BNIP3 protein and stimulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurochem Int. 2006;48:687–695. - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurological examination. Stroke. 1986;17:472–476. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron M, Yu AY, Solway KE, Semenza GL, Sharp FR. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) and its target genes following focal ischaemia in rat brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:4159–4170. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron M, Gidday JM, Yu AY, Semenza GL, Ferriero DM, Sharp FR. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance in neonatal rat brain. Ann Neurol. 2000;48:285–296. - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin M, Nedelec AS, Divoux D, MacKenzie ET, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P. Normobaric hypoxia induces tolerance to focal permanent cerebral ischemia in association with an increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and its target genes, erythropoietin and VEGF, in the adult mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002a;22:393–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
