Expression of endothelin 1 and its receptors in the hypoxic pregnant rat
- PMID: 17554077
- PMCID: PMC1989130
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.061820
Expression of endothelin 1 and its receptors in the hypoxic pregnant rat
Abstract
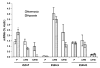
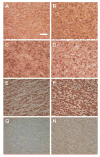
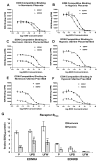
Endothelin 1 (EDN1) plays a primary role in the pathophysiology of hypoxia-induced fetal growth restriction in the rat. In this study we evaluated the effects of chronic maternal hypoxia on the expression of endothelin and its receptors and on receptor binding activity in the uterus and placenta of the rat, in order to elucidate their roles in hypoxia-induced fetal growth restriction. Timed-pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats were maintained in either a normoxic or a normobaric hypoxic (12% O(2)) atmosphere from Gestational Days 18-21. Uterine and placental tissues collected on Gestational Day 21 were assayed for Edn1, Ednra, and Ednrb (endothelin receptors) mRNA expression by real-time quantitative RT-PCR, for localization of EDN1 and its receptors by immunohistochemistry, for EDNRA and EDNRB protein expression by Western blot, and for receptor binding activity by homologous competitive binding assays. EDN1 mRNA expression was significantly increased in the hypoxic placenta, but not in the uterus, compared with normoxic controls. Immunohistochemistry revealed increased EDN1 specifically in the labyrinth of the placenta. Receptor mRNA levels were not significantly affected by hypoxia, but EDNRA protein expression was significantly decreased specifically in the uterine placental beds. Receptor binding decreased significantly in response to hypoxia in all tissues investigated, compared with controls. These results suggest that chronic maternal hypoxia results in increased expression of EDN1 in the placenta but not in the uterus, and that reduced binding activity, rather than regulation of receptor expression, is a mechanism by which these tissues regulate the local hemodynamic response to increased endogenous placental EDN1 in the setting of hypoxia.
Figures
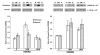
Similar articles
-
Cloprostenol, a prostaglandin F(2alpha) analog, induces hypoxia in rat placenta: BOLD contrast MRI.NMR Biomed. 2007 Feb;20(1):28-39. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1087. NMR Biomed. 2007. PMID: 16947426
-
Altered endothelin receptor binding in response to nitric oxide synthase inhibition in the pregnant rat.Reprod Sci. 2008 Apr;15(4):366-73. doi: 10.1177/1933719107312627. Epub 2008 Mar 6. Reprod Sci. 2008. PMID: 18325929 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic regulation of EDN1, EDNRA, EDNRB, and ECE1 gene expressions in ERN1 knockdown U87 glioma cells.Endocr Regul. 2019 Oct 1;53(4):250-262. doi: 10.2478/enr-2019-0025. Endocr Regul. 2019. PMID: 31734650
-
Upregulation of endothelin receptors A and B in the nitrofen induced hypoplastic lung occurs early in gestation.Pediatr Surg Int. 2010 Jan;26(1):65-9. doi: 10.1007/s00383-009-2514-8. Pediatr Surg Int. 2010. PMID: 19851775
-
Effects of endothelin receptor type-A and type-B antagonists on prostaglandin F2alpha-induced luteolysis of the sheep corpus luteum.Biol Reprod. 2008 Apr;78(4):688-96. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.064105. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Biol Reprod. 2008. PMID: 18077801
Cited by
-
Genome methylation and regulatory functions for hypoxic adaptation in Tibetan chicken embryos.PeerJ. 2017 Oct 6;5:e3891. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3891. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 29018624 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic hypoxia alters fetal cerebrovascular responses to endothelin-1.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;313(2):C207-C218. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00241.2016. Epub 2017 May 31. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28566491 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal PRKAA1 and EDNRA genotypes are associated with birth weight, and PRKAA1 with uterine artery diameter and metabolic homeostasis at high altitude.Physiol Genomics. 2014 Sep 15;46(18):687-97. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00063.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Physiol Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25225183 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory dynamics in the porcine myometrium: global transcriptome analysis, including the effects of PPARγ ligands.BMC Genomics. 2024 Dec 5;25(1):1183. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11083-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39639230 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-dependent vasoconstriction in human uterine artery: application to preeclampsia.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 26;6(1):e16540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016540. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21298073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cervar M, Puerstner P, Kainer F, Desoye G. Endothelin-1 stimulates the proliferation and invasion of first trimester trophoblastic cells in vitro — a possible role in the etiology of pre-eclampsia? J Investig Med. 1996;44:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Shichiri M, Kato H, Marumo F, Hirata Y. Endothelin-1 as an autocrine/paracrine apoptosis survival factor for endothelial cells. Hypertension. 1997;30:1198–1203. - PubMed
-
- De Nucci G, Thomas R, D’Orleans-Juste P, Antunes E, Walder C, Warner TD, Vane JR. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85:9797–9800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fukuroda T, Fujikawa T, Ozaki S, Ishikawa K, Yano M, Nishikibe M. Clearance of circulating endothelin-1 by ETB receptors in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;199:1461–1465. - PubMed
-
- Thaete LG, Neerhof MG, Caplan MS. Endothelin receptor A antagonism prevents hypoxia-induced intrauterine growth restriction in the rat. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;176:73–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

