Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic characterization of the origin-binding domain of the bacteriophage lambda O replication initiator
- PMID: 17554183
- PMCID: PMC2335069
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309107022762
Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic characterization of the origin-binding domain of the bacteriophage lambda O replication initiator
Abstract
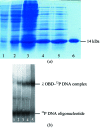
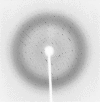
The bacteriophage lambda O protein binds to the lambda replication origin (orilambda) and serves as the primary replication initiator for the viral genome. The binding energy derived from the binding of O to orilambda is thought to help drive DNA opening to facilitate initiation of DNA replication. Detailed understanding of this process is severely limited by the lack of high-resolution structures of O protein or of any lambdoid phage-encoded paralogs either with or without DNA. The production of crystals of the origin-binding domain of lambda O that diffract to 2.5 A is reported. Anomalous dispersion methods will be used to solve this structure.
Figures

References
-
- Alfano, C. & McMacken, R. (1989). J. Biol. Chem.264, 10699–10708. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 760–763.
-
- Cromer, D. T. & Liberman, D. A. (1981). Acta Cryst. A37, 267–268.
-
- Cudney, R., Patel, S., Weisgraber, K., Newhouse, Y. & McPherson, A. (1994). Acta Cryst. D50, 414–423. - PubMed
-
- Denniston-Thompson, K., Moore, D. D., Kruger, K. E., Furth, M. E. & Blattner, F. R. (1977). Science, 198, 1051–1056. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

