Inhibition of opioid release in the rat spinal cord by serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptors
- PMID: 17555728
- PMCID: PMC2377402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.006
Inhibition of opioid release in the rat spinal cord by serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptors
Abstract
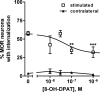
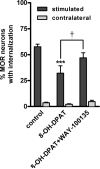
Neurotransmitter receptors that inhibit the release of opioid peptides in the spinal cord may play an important role in modulating pain. Serotonin is an important neurotransmitter in bulbospinal descending pathways, and 5-HT(1) receptors have been shown to inhibit synaptic transmission. Our goal was to determine whether 5-HT(1A) receptors inhibit opioid release in the spinal cord. Opioid release was evoked from rat spinal cord slices by electrically stimulating one dorsal horn, and measured in situ through the internalization of micro-opioid receptors in dorsal horn neurons. Stimulation with 1000 square pulses at 500 Hz produced internalization in 60% of the mu-opioid receptor neurons in the stimulated dorsal horn, but not in the contralateral one. The selective 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-dipropylaminotetralin (8-OH-DPAT) inhibited the evoked mu-opioid receptor internalization by about 50%, with an approximate IC(50) of 50 nM. The effect of 8-OH-DPAT was attributed to inhibition of opioid release and not of the receptor internalization process, because 8-OH-DPAT did not inhibit the internalization induced by incubating the slices with a micro-opioid receptor agonist (endomorphin-2, 100 nM). The selective 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist WAY100135 (10 microM) blocked the inhibition produced by 1 microM 8-OH-DPAT. These results show that 5-HT(1A) receptors inhibit opioid release in the spinal dorsal horn, probably from a subpopulation of enkephalin-containing presynaptic terminals. Therefore, 5-HT(1A) receptors likely decrease the analgesia produced by endogenously released opioids.
Figures
References
-
- Alhaider AA, Wilcox GL. Differential roles of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor subtypes in modulating spinal nociceptive transmission in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993;265:378–385. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Wu G, Kozlov A, Barasi S. The actions of 5-HT1 agonists and antagonists on nociceptive processing in the rat spinal cord: results from behavioural and electrophysiological studies. Brain Res. 1994;661:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Chou J, Tang J, Del Rio J, Yang HY, Costa E. Action of peptidase inhibitors on methionine5-enkephalin-arginine6-phenylalanine7 (YGGFMRF) and methionine5-enkephalin (YGGFM) metabolism and on electroacupuncture antinociception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984;230:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Claustre Y, Benavides J, Scatton B. Potential mechanisms involved in the negative coupling between serotonin 5-HT1A receptors and carbachol-stimulated phosphoinositide turnover in the rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 1991;56:1276–1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

