The risk of malarial infections and disease in Papua New Guinean children
- PMID: 17556601
- PMCID: PMC3740942
The risk of malarial infections and disease in Papua New Guinean children
Abstract
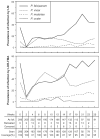
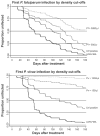
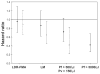
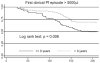
In a treatment re-infection study of 206 Papua New Guinean school children, we examined risk of reinfection and symptomatic malaria caused by different Plasmodium species. Although children acquired a similar number of polymerase chain reaction-detectable Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax infections in six months of active follow-up (P. falciparum = 5.00, P. vivax = 5.28), they were 21 times more likely to develop symptomatic P. falciparum malaria (1.17/year) than P. vivax malaria (0.06/year). Children greater than nine years of age had a reduced risk of acquiring P. vivax infections of low-to-moderate (>150/microL) density (adjusted hazard rate [AHR] = 0.65 and 0.42), whereas similar reductions in risk with age of P. falciparum infection was only seen for parasitemias > 5,000/microL (AHR = 0.49) and symptomatic episodes (AHR = 0.51). Infection and symptomatic episodes with P. malariae and P. ovale were rare. By nine years of age, children have thus acquired almost complete clinical immunity to P. vivax characterized by a very tight control of parasite density, whereas the acquisition of immunity to symptomatic P. falciparum malaria remained incomplete. These observations suggest that different mechanisms of immunity may be important for protection from these malaria species.
Figures

Comment in
-
Acquired immunity in a holoendemic setting of Plasmodium falciparum and p. Vivax malaria.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007 Jun;76(6):995-6. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007. PMID: 17556600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Marsh K, Kinyanjui S. Immune effector mechanisms in malaria. Parasite Immunol. 2006;28:51–60. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Snow RW, Donnelly CA, Marsh K, Newbold C. Immunity to non-cerebral severe malaria is acquired after one or two infections. Nat Med. 1999;5:340–343. - PubMed
-
- Genton B, Al Yaman F, Beck HP, Hii J, Mellor S, Narara A, Gibson N, Smith T, Alpers MP. The epidemiology of malaria in the Wosera area, East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea, in preparation for vaccine trials. I. Malariometric indices and immunity. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1995;89:359–376. - PubMed
-
- Genton B, Al Yaman F, Beck HP, Hii J, Mellor S, Rare L, Ginny M, Smith T, Alpers MP. The epidemiology of malaria in the Wosera area, East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea, in preparation for vaccine trials. II. Mortality and morbidity. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1995;89:377–390. - PubMed
-
- Schofield L, Mueller I. Clinical immunity to malaria. Curr Mol Med. 2006;6:205–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
