Activity and inhibition resistance of a phospholipase-resistant synthetic surfactant in rat lungs
- PMID: 17556674
- PMCID: PMC2176125
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0434OC
Activity and inhibition resistance of a phospholipase-resistant synthetic surfactant in rat lungs
Abstract
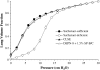
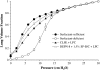
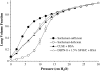
This study investigates the activity and inhibition resistance in excised rat lungs of a novel synthetic surfactant containing the phospholipase-resistant diether phosphonolipid DEPN-8 plus 1.5% bovine surfactant protein (SP)-B/C compared to calf lung surfactant extract (CLSE). DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C surpassed CLSE in normalizing surfactant-deficient pressure-volume (P-V) deflation mechanics in lavaged excised lungs in the presence of phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) or C18:1 lyso-phosphatidylcholine (LPC). DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C had activity equal to CLSE in normalizing P-V mechanics in the absence of inhibitors or in the presence of serum albumin. These physiologic activity findings were directly consistent with surface activity measurements on the pulsating bubble surfactometer. In the absence of inhibitors, DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C and CLSE rapidly reached minimum surface tensions < 1 mN/m (0.5 and 2.5 mg surfactant phospholipid/ml). DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C maintained its high surface activity in the presence of PLA(2), while the surface activity of CLSE was significantly inhibited by exposure to this enzyme. DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C also had greater surface activity than CLSE in the presence of LPC, and the two surfactants had equivalent surface activity in the presence of albumin. DEPN-8 + 1.5% SP-B/C also had slightly greater surface activity than CLSE when exposed to peroxynitrite in pulsating bubble studies. These results support the potential of developing highly active and inhibition-resistant synthetic exogenous surfactants containing DEPN-8 + apoprotein/peptide constituents for use in treating direct pulmonary forms of clinical acute lung injury (ALI) and the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dynamic surface activity of a fully synthetic phospholipase-resistant lipid/peptide lung surfactant.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 17;2(10):e1039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001039. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17940603 Free PMC article.
-
Surface activity of a synthetic lung surfactant containing a phospholipase-resistant phosphonolipid analog of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003 Sep;285(3):L550-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00346.2002. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12902318
-
Surface properties of sulfur- and ether-linked phosphonolipids with and without purified hydrophobic lung surfactant proteins.Chem Phys Lipids. 2005 Oct;137(1-2):77-93. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2005.07.002. Chem Phys Lipids. 2005. PMID: 16109391
-
Content-dependent activity of lung surfactant protein B in mixtures with lipids.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002 Nov;283(5):L897-906. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00431.2001. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12376341 Review.
-
Protein-lipid interactions and surface activity in the pulmonary surfactant system.Chem Phys Lipids. 2006 Jun;141(1-2):105-18. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2006.02.017. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Chem Phys Lipids. 2006. PMID: 16600200 Review.
Cited by
-
Surfactant for pediatric acute lung injury.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008 Jun;55(3):545-75, ix. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2008.02.016. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2008. PMID: 18501754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid access to phospholipid analogs using thiol-yne chemistry.Chem Sci. 2015 Jul 1;6(7):4365-4372. doi: 10.1039/c5sc00653h. Epub 2015 May 19. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29218208 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Contusion: A Clinico-Pathological Entity with Unpredictable Clinical Course.Bull Emerg Trauma. 2013 Jan;1(1):7-16. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2013. PMID: 27162815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell wounding and repair in ventilator injured lungs.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2008 Nov 30;163(1-3):44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2008.06.019. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18638574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic surface activity of a fully synthetic phospholipase-resistant lipid/peptide lung surfactant.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 17;2(10):e1039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001039. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17940603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chess P, Finkelstein JN, Holm BA, Notter RH. Surfactant replacement therapy in lung injury. In: Notter RH, Finkelstein JN, Holm BA, editors. Lung injury: mechanisms, pathophysiology, and therapy. Boca Raton: Taylor Francis Group, Inc; 2005. pp. 617–663.
-
- Notter RH. Lung surfactants: basic science and clinical applications. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 2000.
-
- Kim DK, Fukuda T, Thompson BT, Cockrill B, Hales C, Bonventre JV. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid phospholipase a2 activities are increased in human adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Physiol 1995;269:L109–L118. - PubMed
-
- Holm BA, Kelcher L, Liu M, Sokolowski J, Enhorning G. Inhibition of pulmonary surfactant by phospholipases. J Appl Physiol 1991;71:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Touqui L, Arbibe L. A role for phospholipase a2 in ards pathogenesis. Mol Med Today 1999;5:244–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

