Permeability of homotypic and heterotypic gap junction channels formed of cardiac connexins mCx30.2, Cx40, Cx43, and Cx45
- PMID: 17557922
- PMCID: PMC2836796
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00234.2007
Permeability of homotypic and heterotypic gap junction channels formed of cardiac connexins mCx30.2, Cx40, Cx43, and Cx45
Abstract
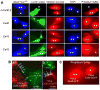
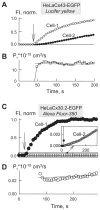
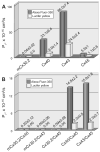
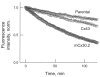
We examined the permeabilities of homotypic and heterotypic gap junction (GJ) channels formed of rodent connexins (Cx) 30.2, 40, 43, and 45, which are expressed in the heart and other tissues, using fluorescent dyes differing in net charge and molecular mass. Combining fluorescent imaging and electrophysiological recordings in the same cell pairs, we evaluated the single-channel permeability (P(gamma)). All homotypic channels were permeable to the anionic monovalent dye Alexa Fluor-350 (AF(350)), but mCx30.2 channels exhibited a significantly lower P(gamma) than the others. The anionic divalent dye Lucifer yellow (LY) remained permeant in Cx40, Cx43, and Cx45 channels, but transfer through mCx30.2 channels was not detected. Heterotypic channels generally exhibited P(gamma) values that were intermediate to the corresponding homotypic channels. P(gamma) values of mCx30.2/Cx40, mCx30.2/Cx43, or mCx30.2/Cx45 heterotypic channels for AF(350) were similar and approximately twofold higher than P(gamma) values of mCx30.2 homotypic channels. Permeabilities for cationic dyes were assessed only qualitatively because of their binding to nucleic acids. All homotypic and heterotypic channel configurations were permeable to ethidium bromide and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. Permeability for propidium iodide was limited only for GJ channels that contain at least one mCx30.2 hemichannel. In summary, we have demonstrated that Cx40, Cx43, and Cx45 are permeant to all examined cationic and anionic dyes, whereas mCx30.2 demonstrates permeation restrictions for molecules with molecular mass over approximately 400 Da. The ratio of single-channel conductance to permeability for AF(350) was approximately 40- to 170-fold higher for mCx30.2 than for Cx40, Cx43, and Cx45, suggesting that mCx30.2 GJs are notably more adapted to perform electrical rather than metabolic cell-cell communication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gap junction permeability: selectivity for anionic and cationic probes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):C600-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00316.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21148413 Free PMC article.
-
Specific permeability and selective formation of gap junction channels in connexin-transfected HeLa cells.J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):805-17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.805. J Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7537274 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac gap junction channels show quantitative differences in selectivity.Circ Res. 2002 Jul 26;91(2):104-11. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000025638.24255.aa. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 12142342
-
Connexin-mediated cardiac impulse propagation: connexin 30.2 slows atrioventricular conduction in mouse heart.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006 Nov;16(8):266-72. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2006.05.002. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2006. PMID: 17055382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cardiac arrhythmias in targeted connexin deficient mice: significance for the arrhythmia field].Z Kardiol. 2000 Dec;89(12):1108-18. doi: 10.1007/s003920070138. Z Kardiol. 2000. PMID: 11201026 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Anisotropic Panglial Coupling Reflects Tonotopic Organization in the Inferior Colliculus.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Nov 27;12:431. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00431. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30542265 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the factors that affect solute permeation of gap junction channels.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Jan;1860(1):96-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 28690048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexins and the kidney.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):R1143-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00808.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20164205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pannexins form gap junctions with electrophysiological and pharmacological properties distinct from connexins.Sci Rep. 2014 May 14;4:4955. doi: 10.1038/srep04955. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24828343 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Asymmetric Flux in Heterotypic Gap Junctions by Pore Shape, Particle Size and Charge.Front Physiol. 2017 Apr 6;8:206. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00206. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28428758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beblo DA, Wang HZ, Beyer EC, Westphale EM, Veenstra RD. Unique conductance, gating, and selective permeability properties of gap junction channels formed by connexin40. Circ Res. 1995;77:813–822. - PubMed
-
- Biegon RP, Atkinson MM, Liu TF, Kam EY, Sheridan JD. Permeance of Novikoff hepatoma gap junctions: quantitative video analysis of dye transfer. J Membr Biol. 1987;96:225–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

