Suppression of conditioning to ambiguous cues by pharmacogenetic inhibition of the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 17558402
- PMCID: PMC2836794
- DOI: 10.1038/nn1919
Suppression of conditioning to ambiguous cues by pharmacogenetic inhibition of the dentate gyrus
Abstract
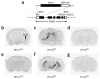
Serotonin receptor 1A knockout (Htr1a(KO)) mice show increased anxiety-related behavior in tests measuring innate avoidance. Here we demonstrate that Htr1a(KO) mice show enhanced fear conditioning to ambiguous conditioned stimuli, a hallmark of human anxiety. To examine the involvement of specific forebrain circuits in this phenotype, we developed a pharmacogenetic technique for the rapid tissue- and cell type-specific silencing of neural activity in vivo. Inhibition of neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala suppressed conditioned responses to both ambiguous and nonambiguous cues. In contrast, inhibition of hippocampal dentate gyrus granule cells selectively suppressed conditioned responses to ambiguous cues and reversed the knockout phenotype. These data demonstrate that Htr1a(KO) mice have a bias in the processing of threatening cues that is moderated by hippocampal mossy-fiber circuits, and suggest that the hippocampus is important in the response to ambiguous aversive stimuli.
Figures
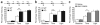



Comment in
-
Ambiguity and anxiety: when a glass half full is empty.Nat Neurosci. 2007 Jul;10(7):807-8. doi: 10.1038/nn0707-807. Nat Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17593939 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Increased fear response to contextual cues in mice lacking the 5-HT1A receptor.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Jan;31(1):101-11. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300774. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 15920501
-
5-HT1A receptor expression during memory formation.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Sep;181(2):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2240-4. Epub 2005 Oct 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15778876
-
Effects of GABA(B), 5-HT(1A), and 5-HT(2) receptor stimulation on activation and inhibition of the rat lateral amygdala following medial geniculate nucleus stimulation in vivo.Brain Res. 2005 Jan 7;1031(1):141-50. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.10.035. Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 15621024
-
Regulation of conditioned and unconditioned fear in rats by 5-HT1A receptors in the dorsal periaqueductal gray.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Mar;89(1):76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 21. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008. PMID: 18076976
-
Lasting increase in serotonin 5-HT1A but not 5-HT4 receptor subtypes in the kindled rat dentate gyrus: dissociation from local presynaptic effects.J Neurochem. 1998 Feb;70(2):850-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70020850.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9453582
Cited by
-
Serotonin homeostasis and serotonin receptors as actors of cortical construction: special attention to the 5-HT3A and 5-HT6 receptor subtypes.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Jun 19;7:93. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00093. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23801939 Free PMC article.
-
Ongoing neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus mediates behavioral responses to ambiguous threat cues.PLoS Biol. 2017 Apr 7;15(4):e2001154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001154. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28388632 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin modulates infraslow oscillation in the dentate gyrus during non-REM sleep.Elife. 2025 Apr 3;13:RP100196. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100196. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40178074 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to the developmental programming of anxiety in serotonin receptor 1A knock-out mice.J Neurosci. 2008 Jun 11;28(24):6250-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5219-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18550767 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation in cortico-amygdala serotonin function and risk for stress-related disease.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008 Sep;32(7):1293-314. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.03.006. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008. PMID: 18439676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gross C, et al. Serotonin1A receptor acts during development to establish normal anxiety-like behaviour in the adult. Nature. 2002;416:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Groenink L, et al. 5-HT1A receptor knockout mice and mice overexpressing corticotropin-releasing hormone in models of anxiety. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003;463:185–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

