The second extracellular loop of alpha2A-adrenoceptors contributes to the binding of yohimbine analogues
- PMID: 17558432
- PMCID: PMC2189838
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707330
The second extracellular loop of alpha2A-adrenoceptors contributes to the binding of yohimbine analogues
Abstract
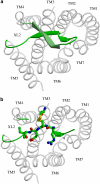
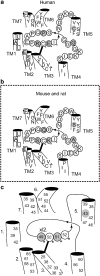
Background and purpose: Rodent alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors bind the classical alpha(2)-antagonists yohimbine and rauwolscine with lower affinity than the human alpha(2A)-adrenoceptor. A serine-cysteine difference in the fifth transmembrane helix (TM; position 5.43) partially explains this, but all determinants of the interspecies binding selectivity are not known. Molecular models of alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors suggest that the second extracellular loop (XL2) folds above the binding cavity and may participate in antagonist binding.
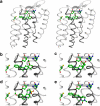
Experimental approach: Amino acids facing the binding cavity were identified using molecular models: side chains of residues 5.43 in TM5 and xl2.49 and xl2.51 in XL2 differ between the mouse and human receptors. Reciprocal mutations were made in mouse and human alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors at positions 5.43, xl2.49 and xl2.51, and tested with a set of thirteen chemically diverse ligands in competition binding assays.
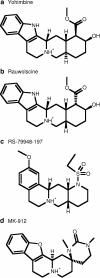
Key results: Reciprocal effects on the binding of yohimbine and rauwolscine in human and mouse alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors were observed for mutations at 5.43, xl2.49 and xl2.51. The binding profile of RS-79948-197 was reversed only by the XL2 substitutions.
Conclusions and implications: Positions 5.43, xl2.49 and xl2.51 are major determinants of the species preference for yohimbine and rauwolscine of the human versus mouse alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors. Residues at positions xl2.49 and xl2.51 determine the binding preference of RS-79948-197 for the human alpha(2A)-adrenoceptor. Thus, XL2 is involved in determining the species preferences of alpha(2A)-adrenoceptors of human and mouse for some antagonists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of the first transmembrane segment of human α(2) -adrenoceptors in the subtype-selective binding of chlorpromazine, spiperone and spiroxatrine.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;164(5):1558-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01520.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21649638 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of alpha2 adrenoceptor ligands at alpha2A and 5-HT1A receptors: the antagonist, atipamezole, and the agonist, dexmedetomidine, are highly selective for alpha2A adrenoceptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998 Aug;358(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/pl00005243. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9750005
-
[Ethyl-3H]RS-79948-197 alpha2-adrenoceptor autoradiography validation in alpha2-adrenoceptor knockout mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Aug 30;497(3):301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.06.065. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15336948
-
Does [3H]2-methoxy-idazoxan (RX 821002) detect more alpha-2-adrenoceptor agonist high-affinity sites than [3H]rauwolscine? A comparison of nine tissues and cell lines.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jun;273(3):1287-94. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. PMID: 7791100
-
Pharmacological facilitation of fear extinction and the search for adjunct treatments for anxiety disorders--the case of yohimbine.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010 Jan;31(1):2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2009.10.003. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20036429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ligands of Adrenergic Receptors: A Structural Point of View.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 24;11(7):936. doi: 10.3390/biom11070936. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34202543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phe369(7.38) at human 5-HT(7) receptors confers interspecies selectivity to antagonists and partial agonists.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Mar;159(5):1069-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00481.x. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19922537 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the first transmembrane segment of human α(2) -adrenoceptors in the subtype-selective binding of chlorpromazine, spiperone and spiroxatrine.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;164(5):1558-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01520.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21649638 Free PMC article.
-
Amphetamine decreases α2C-adrenoceptor binding of [11C]ORM-13070: a PET study in the primate brain.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Dec 13;18(3):pyu081. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu081. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25522417 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that the multiflorine-derived substituted quinazolidine 55P0251 augments insulin secretion and lowers blood glucose via antagonism at α2 -adrenoceptors in mice.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Mar;22(3):290-302. doi: 10.1111/dom.13895. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 31608542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman JD, Trendelenberg AU, MacMillan L, Bernstein D, Limbird L, Starke K, et al. Abnormal regulation of the sympathetic nervous system in alpha2A-adrenergic receptor knockout mice. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56:154–161. - PubMed
-
- Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H.Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure–function relations in G protein-coupled receptors Receptor Molecular Biology 1995Academic Press Inc.: San Diego; 366–427.In: Sealfon SC (ed)
-
- Bissantz C, Bernard P, Hibert M, Rognan D. Protein-based virtual screening of chemical databases. II. Are homology models of G-protein coupled receptors suitable targets. Proteins. 2003;50:5–25. - PubMed
-
- Blaxall HS, Heck DA, Bylund DB. Molecular determinants of the alpha-2D adrenergic receptor subtype. Life Sci. 1993;53:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;7:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

