MicroRNA-mediated feedback and feedforward loops are recurrent network motifs in mammals
- PMID: 17560377
- PMCID: PMC2072999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.018
MicroRNA-mediated feedback and feedforward loops are recurrent network motifs in mammals
Abstract
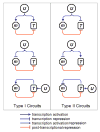
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulatory molecules that participate in diverse biological processes in animals and plants. While thousands of mammalian genes are potentially targeted by miRNAs, the functions of miRNAs in the context of gene networks are not well understood. Specifically, it is unknown whether miRNA-containing networks have recurrent circuit motifs, as has been observed in regulatory networks of bacteria and yeast. Here we develop a computational method that utilizes gene expression data to show that two classes of circuits-corresponding to positive and negative transcriptional coregulation of a miRNA and its targets-are prevalent in the human and mouse genomes. Additionally, we find that neuronal-enriched miRNAs tend to be coexpressed with their target genes, suggesting that these miRNAs could be involved in neuronal homeostasis. Our results strongly suggest that coordinated transcriptional and miRNA-mediated regulation is a recurrent motif to enhance the robustness of gene regulation in mammalian genomes.
Figures

References
-
- Acar M, Becskei A, van Oudenaarden A. Enhancement of cellular memory by reducing stochastic transitions. Nature. 2005;435:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P, Molyneaux BJ, Chen J, Inoue J, Kominami R, Macklis JD. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron. 2005;45:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

