The effect of doxapram on brain imaging in patients with panic disorder
- PMID: 17560768
- PMCID: PMC2695988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2007.04.002
The effect of doxapram on brain imaging in patients with panic disorder
Abstract
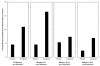
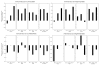
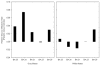
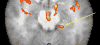
Administration of doxapram hydrochloride, a respiratory stimulant, is experienced by panic disorder patients to be similar to panic attacks but has reduced emotional effect in normal volunteers, thus providing a laboratory model of panic for functional imaging. Six panic patients and seven normal control subjects underwent positron emission tomography with (18)F-deoxyglucose imaging after a single-blinded administration of either doxapram or a placebo saline solution. Saline and doxapram were administered on separate days in counterbalanced order. Patients showed a greater heart rate increase on doxapram relative to saline than controls, indicating differential response. On the saline placebo day, patients had greater prefrontal relative activity than controls. In response to doxapram, patients tended to decrease prefrontal activity more than controls, and increased cingulate gyrus and amygdala activity more than controls. This suggests that panic disorder patients activate frontal inhibitory centers less than controls, a tendency that may lower the threshold for panic.
Figures
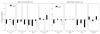
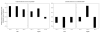

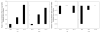
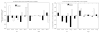
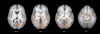
References
-
- Abelson JL, Nesse RM, Weg JG, Curtis GC. Respiratory psychophysiology and anxiety: cognitive intervention in the doxapram model of panic. Psychosom Med. 1996a;58:302–313. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Weg JG, Nesse RM, Curtis GC. Neuroendocrine responses to laboratory panic: cognitive intervention in the doxapram model. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1996b;21:375–90. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Liberzon I, Young EA, Khan S. Cognitive Modulation of the Endocrine Stress Response to a Pharmacological Challenge in Normal and Panic Disorder Subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:668–675. - PubMed
-
- Abelson JL, Khan S, Liberzon I, Young EA. HPA axis activity in patients with panic disorder: review and synthesis of four studies. Depress Anxiety. 2007;24:66–76. - PubMed
-
- Anand A, Shekhar A. Brain imaging studies in mood and anxiety disorders: special emphasis on the amygdala. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2003;985:370–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

