Nuclear migration during retinal development
- PMID: 17560964
- PMCID: PMC2674389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.05.021
Nuclear migration during retinal development
Abstract
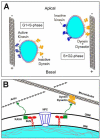
In this review we focus on the mechanisms, regulation, and cellular consequences of nuclear migration in the developing retina. In the nervous system, nuclear migration is prominent during both proliferative and post-mitotic phases of development. Interkinetic nuclear migration is the process where the nucleus oscillates from the apical to basal surfaces in proliferative neuroepithelia. Proliferative nuclear movement occurs in step with the cell cycle, with M-phase being confined to the apical surface and G1-, S-, and G2-phases occurring at more basal locations. Later, following cell cycle exit, some neuron precursors migrate by nuclear translocation. In this mode of cellular migration, nuclear movement is the driving force for motility. Following discussion of the key components and important regulators for each of these processes, we present an emerging model where interkinetic nuclear migration functions to distinguish cell fates among retinal neuroepithelia.
Figures
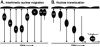

References
-
- Apel ED, Lewis RM, Grady RM, Sanes JR. Syne-1, a dystrophin- and Klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:31986–95. - PubMed
-
- Baye LM, Link BA. Examining interkinetic nuclear migration during retinal development. FASEB JOURNAL. 2005;19:A1367. abstract.
-
- Bhide PG. Cell cycle kinetics in the embryonic mouse corpus striatum. J Comp Neurol. 1996;374:506–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

