Sp1 and Sp3 control constitutive expression of the human NHE2 promoter by interactions with the proximal promoter and the transcription initiation site
- PMID: 17561809
- PMCID: PMC2267401
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070364
Sp1 and Sp3 control constitutive expression of the human NHE2 promoter by interactions with the proximal promoter and the transcription initiation site
Abstract
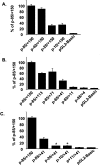
We have previously cloned the human Na+/H+ exchanger NHE2 gene and its promoter region. In the present study, the regulatory elements responsible for the constitutive expression of NHE2 were studied. Transient transfection assays revealed that the -40/+150 promoter region contains the core promoter responsible for the optimal promoter activity. A smaller fragment, -10/+40, containing the TIS (transcription initiation site) showed minimal activity. We identified a palindrome that overlaps the TIS and binds to the transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. Mutations in the 5' flank of the palindrome abolished the Sp1/Sp3 interaction and reduced promoter activity by approx. 45%. In addition, a conserved GC-box centered at -25 was found to play a critical role in basal promoter activity and also interacted with Sp1 and Sp3. An internal deletion in the GC-box severely reduced the promoter activity. Sp1/Sp3 binding to these elements was established using gel-mobility shift assays, confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation and co-transfections in Drosophila SL2 cells. Furthermore, we identified two positive regulatory elements in the DNA region corresponding to the 5'-UTR (5'-untranslated region). The results in the present study indicate that Sp1 and Sp3 are required for constitutive NHE2 expression and that the positive regulatory elements of the 5'-UTR may co-operate with the 5'-flanking region to achieve the optimal promoter activity.
Figures






References
-
- Counillon L., Pouyssegur J. The expanding family of eucaryotic Na+/H+ exchangers. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Orlowski J., Grinstein S. Diversity of the mammalian sodium/proton exchanger SLC9 gene family. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:549–565. - PubMed
-
- Zachos N. C., Tse M., Donowitz M. Molecular physiology of intestinal Na+/H+ exchange. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005;67:411–443. - PubMed
-
- Kiela P. R., Xu H., Ghishan F. K. Apical Na+/H+ exchangers in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006;57(Suppl. 7):51–79. - PubMed
-
- Gawenis L. R., Stien X., Shull G. E., Schultheis P. J., Woo A. L., Walker N. M., Clarke L. L. Intestinal NaCl transport in NHE2 and NHE3 knockout mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002;282:G776–G784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

