Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death
- PMID: 17562483
- PMCID: PMC2117903
- DOI: 10.1080/01926230701320337
Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death
Abstract
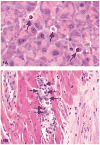
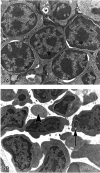
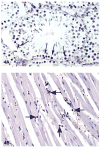
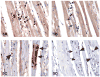
The process of programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is generally characterized by distinct morphological characteristics and energy-dependent biochemical mechanisms. Apoptosis is considered a vital component of various processes including normal cell turnover, proper development and functioning of the immune system, hormone-dependent atrophy, embryonic development and chemical-induced cell death. Inappropriate apoptosis (either too little or too much) is a factor in many human conditions including neurodegenerative diseases, ischemic damage, autoimmune disorders and many types of cancer. The ability to modulate the life or death of a cell is recognized for its immense therapeutic potential. Therefore, research continues to focus on the elucidation and analysis of the cell cycle machinery and signaling pathways that control cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. To that end, the field of apoptosis research has been moving forward at an alarmingly rapid rate. Although many of the key apoptotic proteins have been identified, the molecular mechanisms of action or inaction of these proteins remain to be elucidated. The goal of this review is to provide a general overview of current knowledge on the process of apoptosis including morphology, biochemistry, the role of apoptosis in health and disease, detection methods, as well as a discussion of potential alternative forms of apoptosis.
Figures



References
-
- Arur S, Uche UE, Rezaul K, Fong M, Scranton V, Cowan AE, Mohler W, Han DK. Annexin I is an endogenous ligand that mediates apoptotic cell engulfment. Dev Cell. 2003;4:587–98. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–8. - PubMed
-
- Barry M, Bleackley RC. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: all roads lead to death. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:401–9. - PubMed
-
- Bedner E, Li X, Gorczyca W, Melamed MR, Darzynkiewicz Z. Analysis of apoptosis by laser scanning cytometry. Cytometry. 1999;35:181–95. - PubMed
-
- Bortner CD, Oldenburg NB, Cidlowski JA. The role of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1995;5:21–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

