Effect of fluoroquinolone treatment on growth of and toxin production by epidemic and nonepidemic clostridium difficile strains in the cecal contents of mice
- PMID: 17562807
- PMCID: PMC1932513
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01582-06
Effect of fluoroquinolone treatment on growth of and toxin production by epidemic and nonepidemic clostridium difficile strains in the cecal contents of mice
Abstract
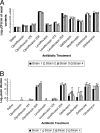
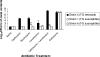
Several recent outbreaks of Clostridium difficile-associated disease (CDAD) have been attributed to the emergence of an epidemic strain with increased resistance to fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Some clinical studies have suggested that fluoroquinolones with enhanced antianaerobic activity (i.e., gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin) may have a greater propensity to induce CDAD than ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin do. We examined the effects of subcutaneous fluoroquinolone treatment on in vitro growth of and toxin production by epidemic and nonepidemic C. difficile isolates in cecal contents of mice and evaluated the potential for these agents to inhibit fluoroquinolone-susceptible isolates during treatment. When C. difficile isolates were inoculated into cecal contents collected 2 days after the final antibiotic dose, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin promoted significantly more growth and toxin production than ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin did. During treatment, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin inhibited growth of fluoroquinolone-susceptible but not fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates. Ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin promoted growth of C. difficile when administered at higher doses (i.e., 20 times the human dose in mg/kg of body weight), and levofloxacin inhibited growth of fluoroquinolone-susceptible, but not fluoroquinolone-resistant, C. difficile isolates when administered in combination with ceftriaxone. Thus, fluoroquinolones with enhanced antianaerobic activity (i.e., gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin) promoted C. difficile growth to a greater extent than did ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin in this model. However, our findings suggest that fluoroquinolones may exert selective pressure favoring the emergence of epidemic fluoroquinolone-resistant C. difficile strains by inhibiting fluoroquinolone-susceptible but not fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates during treatment and that agents such as levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin can exert such selective pressure when administered in combination with antibiotics that disrupt the anaerobic microflora.
Figures
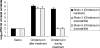
References
-
- Borriello, S. P., F. E. Barclay, and A. R. Welch. 1988. Evaluation of the predictive capability of an in-vitro model of colonization resistance to Clostridium difficile infection. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1:61-64.
-
- Gaynes, R., D. Rimland, E. Killum, K. Lowery, T. M. Johnson, G. Killgore, and F. C. Tenover. 2004. Outbreak of Clostridium difficile infection in a long-term care facility: association with gatifloxacin use. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:640-645. - PubMed
-
- Gerding, D. N. 2004. Clindamycin, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: this is an antimicrobial resistance problem. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:646-648. - PubMed
-
- Golledge, C. L., C. F. Carson, G. L. O'Neill, R. A. Bowman, and T. V. Riley. 1992. Ciprofloxacin and Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 30:141-147. - PubMed
-
- Johnson, S., M. H. Samore, K. A. Farrow, G. E. Killgore, F. C. Tenover, D. Lyras, J. I. Rood, P. DeGirolami, A. L. Baltch, M. E. Rafferty, S. M. Pear, and D. N. Gerding. 1999. Epidemics of diarrhea caused by a clindamycin-resistant strain of Clostridium difficile in four hospitals. N. Engl. J. Med. 341:1645-1651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

