Mice with a disruption of the imprinted Grb10 gene exhibit altered body composition, glucose homeostasis, and insulin signaling during postnatal life
- PMID: 17562854
- PMCID: PMC1952119
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02087-06
Mice with a disruption of the imprinted Grb10 gene exhibit altered body composition, glucose homeostasis, and insulin signaling during postnatal life
Abstract
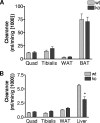
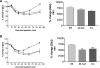
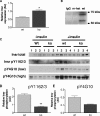
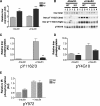
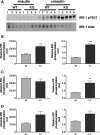
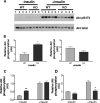
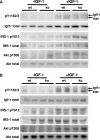
The Grb10 adapter protein is capable of interacting with a variety of receptor tyrosine kinases, including, notably, the insulin receptor. Biochemical and cell culture experiments have indicated that Grb10 might act as an inhibitor of insulin signaling. We have used mice with a disruption of the Grb10 gene (Grb10Delta2-4 mice) to assess whether Grb10 might influence insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis in vivo. Adult Grb10Delta2-4 mice were found to have improved whole-body glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, as well as increased muscle mass and reduced adiposity. Tissue-specific changes in insulin receptor tyrosine phosphorylation were consistent with a model in which Grb10, like the closely related Grb14 adapter protein, prevents specific protein tyrosine phosphatases from accessing phosphorylated tyrosines within the kinase activation loop. Furthermore, insulin-induced IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation was enhanced in Grb10Delta2-4 mutant animals, supporting a role for Grb10 in attenuation of signal transmission from the insulin receptor to IRS-1. We have previously shown that Grb10 strongly influences growth of the fetus and placenta. Thus, Grb10 forms a link between fetal growth and glucose-regulated metabolism in postnatal life and is a candidate for involvement in the process of fetal programming of adult metabolic health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual ablation of Grb10 and Grb14 in mice reveals their combined role in regulation of insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Sep;23(9):1406-14. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0386. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19541746 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin and type 1 insulin-like growth factor signaling and action by the Grb10/14 and SH2B1/B2 adaptor proteins.FEBS J. 2013 Feb;280(3):794-816. doi: 10.1111/febs.12080. Epub 2013 Jan 2. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23190452 Review.
-
Grb7, Grb10 and Grb14, encoding the growth factor receptor-bound 7 family of signalling adaptor proteins have overlapping functions in the regulation of fetal growth and post-natal glucose metabolism.BMC Biol. 2024 Sep 30;22(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02018-5. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39343875 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral disruption of the Grb10 gene enhances insulin signaling and sensitivity in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Sep;27(18):6497-505. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00679-07. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17620412 Free PMC article.
-
Grb10 exceeding the boundaries of a common signaling adapter.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:603-18. doi: 10.2741/1227. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766395 Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of growth factor receptor-binding protein 10 in the pancreas enhances β-cell proliferation and protects mice from streptozotocin-induced β-cell apoptosis.Diabetes. 2012 Dec;61(12):3189-98. doi: 10.2337/db12-0249. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22923474 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic imprinting and its effects on postnatal growth and adult metabolism.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Oct;76(20):4009-4021. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03197-z. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31270580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The insulin signalling network.Nat Metab. 2025 Aug 11. doi: 10.1038/s42255-025-01349-z. Online ahead of print. Nat Metab. 2025. PMID: 40789980 Review.
-
The insulin receptor: both a prototypical and atypical receptor tyrosine kinase.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Mar 1;5(3):a008946. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008946. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23457259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Profiling of Skeletal Muscle from Black Muscovy Duck at Different Growth Stages Using RNA-seq.Genes (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;11(10):1228. doi: 10.3390/genes11101228. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Accili, D., J. Drago, E. J. Lee, M. D. Johnson, M. H. Cool, P. Salvatore, L. D. Asico, P. A. Jose, S. I. Taylor, and H. Westphal. 1996. Early neonatal death in mice homozygous for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene. Nat. Genet. 12:106-109. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud, P., D. Monk, M. Hitchins, E. Gordon, W. Dean, C. V. Beechey, J. Peters, W. Craigen, M. Preece, P. Stanier, G. E. Moore, and G. Kelsey. 2003. Conserved methylation imprints in the human and mouse GRB10 genes with divergent allelic expression suggests differential reading of the same mark. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12:1005-1019. - PubMed
-
- Asante-Appiah, E., and B. P. Kennedy. 2003. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: the quest for negative regulators of insulin action. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284:E663-E670. - PubMed
-
- Bence, K. K., M. Delibegovic, B. Xue, C. Z. Gorgun, G. S. Hotamisligil, B. G. Neel, and B. B. Kahn. 2006. Neuronal PTP1B regulates body weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat. Med. 12:917-924. - PubMed
-
- Bennett, W. R., T. E. Crew, J. M. W. Slack, and A. Ward. 2003. Structural-proliferative units and organ growth: effects of insulin-like growth factor 2 on growth of colon and skin. Development 130:1079-1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
