Protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTP1B, expression and activity in rat corneal endothelial cells
- PMID: 17563729
- PMCID: PMC2768764
Protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTP1B, expression and activity in rat corneal endothelial cells
Abstract
Purpose: The current studies were conducted to determine whether the protein tyrosine phosphatase, PTP1B, plays a role in regulating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Tyr992 phosphorylation and cell cycle entry in rat corneal endothelial cells.
Methods: Corneas were obtained from male Sprague-Dawley rats. PTP1B mRNA and protein expression were compared in confluent and subconfluent cells by RT-PCR and western blots. Immunocytochemistry was used to determine the subcellular localization of both PTP1B and EGFR following epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation. Western blots were used to analyze the time-dependent effect of EGF on phosphorylation of EGFR Tyr992 plus or minus CinnGEL 2Me, an inhibitor of PTP1B activity. The effect of PTP1B inhibition on cell cycle entry was determined by calculating the percent of Ki67-positive cells following EGF treatment.
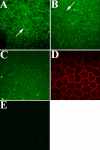
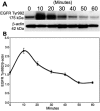
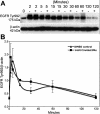
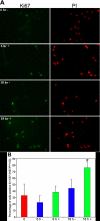
Results: PTP1B mRNA expression was similar in confluent and subconfluent cells, but PTP1B protein was expressed at 3 fold higher levels in subconfluent cells. Positive staining for PTP1B was localized in vesicular structures below the plasma membrane. EGFR staining was located at cell-cell borders in untreated endothelium, but was mainly cytoplasmic by 15 min after EGF treatment. In control cultures, phosphorylation of EGFR Tyr992 peaked by 5 min following EGF stimulation and rapidly decreased to basal levels by 30 min. In cultures pretreated with CinnGEL 2Me, Tyr992 phosphorylation peaked 2 min following EGF addition and was consistently sustained at a higher level than controls until 60 min after treatment. By 18 h following EGF treatment, cultures pretreated with CinnGEL 2Me exhibited a 1.7 fold increase in the number of Ki67-positive cells compared with control cultures.
Conclusions: Comparison of PTP1B mRNA and protein levels indicates that PTP1B expression is regulated mainly at the protein level and is higher in subconfluent cells. PTP1B was located in vesicles below the plasma membrane. The fact that EGFR is internalized in response to EGF stimulation suggests that it could interact with and be regulated by PTP1B. The ability of PTP1B inhibitor to sustain EGFR Tyr992 phosphorylation and increase the number of Ki67-positive cells indicates that PTP1B plays a role in the negative regulation of EGF-induced signaling and helps suppress cell cycle entry.
Figures
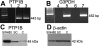

Similar articles
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B) helps regulate EGF-induced stimulation of S-phase entry in human corneal endothelial cells.Mol Vis. 2008 Jan 16;14:61-70. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18253097 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SOV-induced phosphatase inhibition and expression of protein tyrosine phosphatases in rat corneal endothelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2005 Nov;81(5):570-80. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2005.03.015. Epub 2005 Jun 13. Exp Eye Res. 2005. PMID: 15950220
-
Mechanisms of mitotic inhibition in corneal endothelium: contact inhibition and TGF-beta2.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Jul;43(7):2152-9. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 12091410
-
The role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the cell-cell interactions, junctional permeability and cell cycle control in post-confluent bovine corneal endothelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2007 Aug;85(2):259-69. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.04.012. Epub 2007 May 13. Exp Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17624326
-
Recent development of small molecular specific inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B.Med Res Rev. 2007 Jul;27(4):553-73. doi: 10.1002/med.20079. Med Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17039461 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs)-1B with c-Met receptor and modulation of corneal epithelial wound healing.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008 Jul;49(7):2927-35. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-0709. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18579758 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR may couple moderate alcohol consumption to increased breast cancer risk.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2009 Oct 5;1:31-8. doi: 10.2147/bctt.s6254. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2009. PMID: 24367161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B (PTP1B) helps regulate EGF-induced stimulation of S-phase entry in human corneal endothelial cells.Mol Vis. 2008 Jan 16;14:61-70. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18253097 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B regulates migration of ARPE-19 cells through EGFR/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Ophthalmol. 2015 Oct 18;8(5):891-7. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.05.07. eCollection 2015. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26558197 Free PMC article.
-
EGF-conditioned M1 macrophages Convey reduced inflammation into corneal endothelial cells through exosomes.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 22;10(5):e26800. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26800. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38434401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joyce NC. Proliferative capacity of the corneal endothelium. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2003;22:359–89. - PubMed
-
- Joyce NC. Cell cycle status in human corneal endothelium. Exp Eye Res. 2005;81:629–38. - PubMed
-
- Jumblatt MM, Matkin ED, Neufeld AH. Pharmacological regulation of morphology and mitosis in cultured rabbit corneal endothelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988;29:586–93. - PubMed
-
- Savion N, Isaacs JD, Shuman MA, Gospodarowicz D. Proliferation and differentiation of bovine corneal endothelial cells in culture. Metab Pediatr Syst Ophthalmol. 1982;6:305–20. - PubMed
-
- Woost PG, Jumblatt MM, Eiferman RA, Schultz GS. Growth factors and corneal endothelial cells: II. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor from bovine corneal endothelial cells. Cornea. 1992;11:11–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
