Effect of lead on ERK activity and the protective function of bFGF in rat primary culture astroglia
- PMID: 17565513
- PMCID: PMC1879161
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2007.B0422
Effect of lead on ERK activity and the protective function of bFGF in rat primary culture astroglia
Abstract
Objective: To observe the effects of lead on levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase (p-ERK) in the cytoplasm of primary cultures of rat astroglial cells and the possible protective effect of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) on lead-induced effects.
Methods: The primary astroglia cells from 1~6 d old Wistar rats were cultured. The cells pretreated with the MEK1 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1) inhibitor PD98059 and bFGF, respectively, were exposed to Pb acetate of different concentrations for different times. Western blotting and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods were used to detect the protein and mRNA expressions of ERK.
Results: mRNA expression for ERK peaked 15 min after initiation of lead exposure (P<0.05) and protein expression of p-ERK peaked at 30 min (P<0.05). ERK mRNA levels and p-ERK protein levels returned to baseline after 60 and 120 min of lead exposure, respectively (P>0.05). The increase in p-ERK levels in lead-treated cells could be inhibited by PD098059. Activation of ERK in the cells by lead was prevented by pretreatment with bFGF. Total ERK protein levels did not change under the same experimental conditions (P>0.05).
Conclusion: Low-level lead exposure resulted in transient activation of ERK through the MEK pathway, which then returned to basal levels in the continued presence of lead. Exogenous bFGF protected ERK signaling components in astroglia from lead poisoning.
Figures





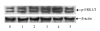

Similar articles
-
Induction of transforming growth factor-beta1 by basic fibroblast growth factor in rat C6 glioma cells and astrocytes is mediated by MEK/ERK signaling and AP-1 activation.J Neurosci Res. 2007 Apr;85(5):1033-45. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21182. J Neurosci Res. 2007. PMID: 17335076
-
Dexamethasone inhibits basic fibroblast growth factor-stimulated gastric epithelial cell proliferation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Oct 1;76(7):841-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.010. Epub 2008 Jul 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18692028
-
Noradrenergic regulation of period1 expression in spinal astrocytes is involved in protein kinase A, c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation mediated by α1- and β2-adrenoceptors.Neuroscience. 2011 Jun 30;185:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.04.024. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21524690
-
PDGFRβ triggered by bFGF promotes the proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells via p-ERK signalling.Cell Biol Int. 2012 Oct 1;36(10):945-50. doi: 10.1042/CBI20110657. Cell Biol Int. 2012. PMID: 22731705
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation predominantly in Müller cells of retina with endotoxin-induced uveitis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Apr;43(4):907-11. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 11923227
Cited by
-
The History, Status, Gaps, and Future Directions of Neurotoxicology in China.Environ Health Perspect. 2016 Jun;124(6):722-32. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1409566. Epub 2016 Jan 29. Environ Health Perspect. 2016. PMID: 26824332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

