Fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor in CSF: a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 17565664
- PMCID: PMC1896177
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-7-14
Fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor in CSF: a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may be valuable for exploring protein markers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The prospect of early detection and treatment, to slow progression, holds hope for aging populations with increased average lifespan. The aim of the present study was to investigate candidate CSF biological markers in patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD and compare them with age-matched normal control subjects.
Methods: We applied proteomics approaches to analyze CSF samples derived from 27 patients with AD, 3 subjects with MCI and 30 controls. The AD group was subdivided into three groups by clinical severity according to clinical dementia rating (CDR), a well known clinical scale for dementia.
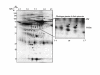
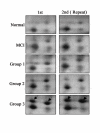
Results: We demonstrated an elevated level of fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor protein in CSF from patients with mild cognitive impairment and AD compared to the age-matched normal subjects. Moreover, its expression was more prominent in the AD group than in the MCI and correlated with disease severity and progression. In contrast, fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor protein was detected very low in the age-matched normal group.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the CSF level of fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor may be a candidate biomarker for AD.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson G, Brane D, Block W, Kammen DP, Gurklis J, Peters JL, Wyatt RJ, Kirch DG, Ghanbari HA, Merril CR. Cerebrospinal fluid protein variations in common to Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. Appl Theor Electrophor. 1992;3:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Sjögren M, Davidsson P, Gottfries J, Vanderstichele H, Edman A, Vanmechelen E, Wallin A, Blenow K. The cerebrospinal fluid levels of tau, growth-associated protein-43 and soluble amyloid precursor protein correlate in Alzheimer's disease, reflecting a common pathophysiological process. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2001;12:257–264. doi: 10.1159/000051268. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

