Postprocessing of genealogical trees
- PMID: 17565950
- PMCID: PMC2013683
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.071910
Postprocessing of genealogical trees
Abstract
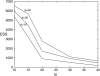
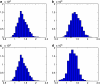
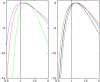
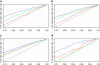
We consider inference for demographic models and parameters based upon postprocessing the output of an MCMC method that generates samples of genealogical trees (from the posterior distribution for a specific prior distribution of the genealogy). This approach has the advantage of taking account of the uncertainty in the inference for the tree when making inferences about the demographic model and can be computationally efficient in terms of reanalyzing data under a wide variety of models. We consider a (simulation-consistent) estimate of the likelihood for variable population size models, which uses importance sampling, and propose two new approximate likelihoods, one for migration models and one for continuous spatial models.
Figures


References
-
- Bahlo, M., and R. C. Griffiths, 1998. Inference from gene trees in a subdivided population. Theor. Popul. Biol. 57: 79–95. - PubMed
-
- Brooks, S. P., I. Manopoulou and B. C. Emerson, 2007. Assessing the affect of genetic mutation: a Bayesian framework for determining population history from DNA sequence data, pp. 25–50 in Bayesian Statistics 8, edited by J. M. Bernardo, M. J. Bayarri, J. O. Berger, A. P. Dawid, D. Heckerman, A. F. M. Smith and M. West. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
-
- Coop, G., and R. C. Griffiths, 2004. Ancestral inference on gene trees under selection. Theor. Popul. Biol. 66: 219–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

