Synapsis-defective mutants reveal a correlation between chromosome conformation and the mode of double-strand break repair during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis
- PMID: 17565963
- PMCID: PMC1950611
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.076968
Synapsis-defective mutants reveal a correlation between chromosome conformation and the mode of double-strand break repair during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis
Abstract
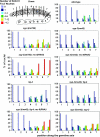
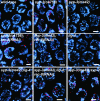
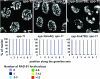
SYP-3 is a new structural component of the synaptonemal complex (SC) required for the regulation of chromosome synapsis. Both chromosome morphogenesis and nuclear organization are altered throughout the germlines of syp-3 mutants. Here, our analysis of syp-3 mutants provides insights into the relationship between chromosome conformation and the repair of meiotic double-strand breaks (DSBs). Although crossover recombination is severely reduced in syp-3 mutants, the production of viable offspring accompanied by the disappearance of RAD-51 foci suggests that DSBs are being repaired in these synapsis-defective mutants. Our studies indicate that once interhomolog recombination is impaired, both intersister recombination and nonhomologous end-joining pathways may contribute to repair during germline meiosis. Moreover, our studies suggest that the conformation of chromosomes may influence the mode of DSB repair employed during meiosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptonemal Complex Central Region Proteins Promote Localization of Pro-crossover Factors to Recombination Events During Caenorhabditis elegans Meiosis.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):395-409. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302625. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31431470 Free PMC article.
-
Synapsis-dependent and -independent mechanisms stabilize homolog pairing during meiotic prophase in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2002 Sep 15;16(18):2428-42. doi: 10.1101/gad.1011602. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12231631 Free PMC article.
-
CRA-1 uncovers a double-strand break-dependent pathway promoting the assembly of central region proteins on chromosome axes during C. elegans meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2008 Jun 6;4(6):e1000088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000088. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18535664 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination in Caenorhabditis elegans.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):607-21. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1146-x. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674149 Review.
-
Female Meiosis: Synapsis, Recombination, and Segregation in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2018 Mar;208(3):875-908. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300081. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29487146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SPR-5 is a histone H3K4 demethylase with a role in meiotic double-strand break repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 2;108(31):12805-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102298108. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21768382 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating chromosomal movement by the cochaperone FKB-6 ensures timely pairing and synapsis.J Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;216(2):393-408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201606126. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28077446 Free PMC article.
-
The MAP kinase pathway coordinates crossover designation with disassembly of synaptonemal complex proteins during meiosis.Elife. 2016 Feb 27;5:e12039. doi: 10.7554/eLife.12039. Elife. 2016. PMID: 26920220 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptonemal Complex Central Region Proteins Promote Localization of Pro-crossover Factors to Recombination Events During Caenorhabditis elegans Meiosis.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):395-409. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302625. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31431470 Free PMC article.
-
CRL4 regulates recombination and synaptonemal complex aggregation in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline.PLoS Genet. 2019 Nov 18;15(11):e1008486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008486. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31738749 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergerat, A., B. de Massy, D. Gadelle, P. C. Varoutas, A. Nicolas et al., 1997. An atypical topoisomerase II from Archaea with implications for meiotic recombination. Nature 386: 414–417. - PubMed
-
- Colaiácovo, M. P., A. J. MacQueen, E. Martinez-Perez, K. McDonald, A. Adamo et al., 2003. Synaptonemal complex assembly in C. elegans is dispensable for loading strand-exchange proteins but critical for proper completion of recombination. Dev. Cell 5: 463–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

