Probing the role of the histidine 759 ligand in cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase
- PMID: 17567043
- PMCID: PMC3113539
- DOI: 10.1021/bi700341y
Probing the role of the histidine 759 ligand in cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase
Abstract
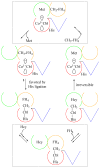
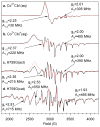
Cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase (MetH) of Escherichia coli is a 136 kDa, modular enzyme that undergoes large conformational changes as it uses a cobalamin cofactor as a donor or acceptor in three separate methyl transfer reactions. At different points during the reaction cycle, the coordination to the cobalt of the cobalamin changes; most notably, the imidazole side chain of His759 that coordinates to the cobalamin in the "His-on" state can dissociate to produce a "His-off" state. Here, two distinct species of the cob(II)alamin-bound His759Gly variant have been identified and separated. Limited proteolysis with trypsin was employed to demonstrate that the two species differ in protein conformation. Magnetic circular dichroism and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopies were used to show that the two species also differ with respect to the axial coordination to the central cobalt ion of the cobalamin cofactor. One form appears to be in a conformation poised for reductive methylation with adenosylmethionine; this form was readily reduced to cob(I)alamin and subsequently methylated [albeit yielding a unique, five-coordinate methylcob(III)alamin species]. Our spectroscopic data revealed that this form contains a five-coordinate cob(II)alamin species, with a water molecule as an axial ligand to the cobalt. The other form appears to be in a catalytic conformation and could not be reduced to cob(I)alamin under any of the conditions tested, which precluded conversion to the methylcob(III)alamin state. This form was found to possess an effectively four-coordinate cob(II)alamin species that has neither water nor histidine coordinated to the cobalt center. The formation of this four-coordinate cob(II)alamin "dead-end" species in the His759Gly variant illustrates the importance of the His759 residue in governing the equilibria between the different conformations of MetH.
Figures











References
-
- Goulding CW, Postigo D, Matthews RG. Cobalamin-Dependent Methionine Syntahse Is a Modular Protein with Distinct Regions for Binding Homocysteine, Methyltetrahydrofolate, Cobalamin, and Adenosylmethionine. Biochemistry. 1997;36:8082–8091. - PubMed
-
- Drummond JT, Huang S, Blumenthal RM, Matthews RG. Assignment of Enzymatic Function to Specific Protein Regions of Cobalamin-Dependent Methionine Synthase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1993;32:9290–9295. - PubMed
-
- Hall DA, Jordan-Starck TC, Loo RO, Ludwig ML, Matthews RG. Interaction of Flavodoxin with Cobalamin-Dependent Methionine Synthase. Biochemistry. 2000;39:10711–10719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

