Cockayne syndrome B protein stimulates apurinic endonuclease 1 activity and protects against agents that introduce base excision repair intermediates
- PMID: 17567611
- PMCID: PMC1919475
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm404
Cockayne syndrome B protein stimulates apurinic endonuclease 1 activity and protects against agents that introduce base excision repair intermediates
Abstract
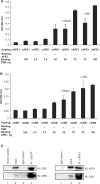
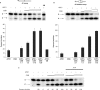
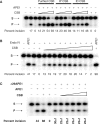
The Cockayne syndrome B (CSB) protein--defective in a majority of patients suffering from the rare autosomal disorder CS--is a member of the SWI2/SNF2 family with roles in DNA repair and transcription. We demonstrate herein that purified recombinant CSB and the major human apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease, APE1, physically and functionally interact. CSB stimulates the AP site incision activity of APE1 on normal (i.e. fully paired) and bubble AP-DNA substrates, with the latter being more pronounced (up to 6-fold). This activation is ATP-independent, and specific for the human CSB and full-length APE1 protein, as no CSB-dependent stimulation was observed with Escherichia coli endonuclease IV or an N-terminal truncated APE1 fragment. CSB and APE1 were also found in a common protein complex in human cell extracts, and recombinant CSB, when added back to CSB-deficient whole cell extracts, resulted in increased total AP site incision capacity. Moreover, human fibroblasts defective in CSB were found to be hypersensitive to both methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) and 5-hydroxymethyl-2'-deoxyuridine, agents that introduce base excision repair (BER) DNA substrates/intermediates.
Figures
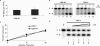

References
-
- Lehmann AR. DNA repair-deficient diseases, xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne syndrome and trichothiodystrophy. Biochimie. 2003;85:1101–1111. - PubMed
-
- Cleaver JE. Cancer in xeroderma pigmentosum and related disorders of DNA repair. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:564–573. - PubMed
-
- Troelstra C, van Gool A, de Wit J, Vermeulen W, Bootsma D, Hoeijmakers JH. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992;71:939–953. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

