Upregulation of PD-1 expression on circulating and intrahepatic hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells associated with reversible immune dysfunction
- PMID: 17567698
- PMCID: PMC1951397
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00409-07
Upregulation of PD-1 expression on circulating and intrahepatic hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ T cells associated with reversible immune dysfunction
Abstract
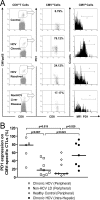
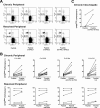
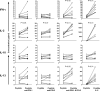
Infection with hepatitis C virus (HCV) is associated with persistence in the majority of individuals. We demonstrate here that the inhibitory molecule programmed death-1 (PD-1) is significantly upregulated on total and HCV-specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in the peripheral blood and livers of patients with chronic infection compared to subjects with spontaneous HCV resolution, patients with nonviral liver disease, and normal controls. PD-1 expression on cytomegalovirus-specific CTLs also varies according to HCV status and is highest in patients with chronic infection. HCV-specific CTLs that are PD-1(high) express higher levels of the senescence marker CD57 than PD-1(low) CTLs, and CD57 expression is greater in chronic than in resolved infection. In vitro blockade of PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies specific to its ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2) results in restoration of functional competence (proliferation and gamma interferon and interleukin-2 secretion) of HCV-specific CTLs, including those residing in the liver. This reversal of CTL exhaustion is evident even in individuals who lack HCV-specific CD4(+) T-cell help. Our data indicate that the PD-1/PD-L pathway is critical in persistent HCV infection in humans and represents a potential novel target for restoring function of exhausted HCV-specific CTLs.
Figures

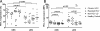
References
-
- Appay, V., P. R. Dunbar, M. Callan, P. Klenerman, G. M. A. Gillespie, L. Papagno, G. S. Ogg, et al. 2002. Memory CD8+ T cells vary in differentiation phenotype in different persistent virus infections. Nat. Med. 8:379-385. - PubMed
-
- Bailer, R. T., A. Holloway, J. Sun, J. B. Margolick, M. Martin, J. Kostman, and L. J. Montaner. 1999. IL-13 and IFN-γ secretion by activated T cells in HIV-1 infection associated with viral suppression and a lack of disease progression. J. Immunol. 162:7534-7542. - PubMed
-
- Barber, D. L., E. J. Wherry, D. Masopust, B. Zhu, J. P. Allison, A. H. Sharpe, G. J. Freeman, and R. Ahmed. 2006. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439:682-687. - PubMed
-
- Boettler, T., H. C. Spangenberg, C. Neumann-Haefelin, E. Panther, S. Urbani, C. Ferrari, H. E. Blum, F. von Weizsacker, and R. Thimme. 2005. T cells with a CD4+ CD25+ regulatory phenotype suppress in vitro proliferation of virus-specific CD8+ T cells during chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 79:7860-7867. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bowen, D. G., and C. M. Walker. 2005. Adaptive immune responses in acute and chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 436:946-952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

