Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates cholesterol metabolism for synapse development
- PMID: 17567802
- PMCID: PMC6672445
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0690-07.2007
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates cholesterol metabolism for synapse development
Abstract
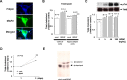
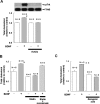
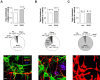
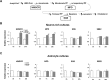
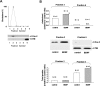
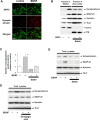
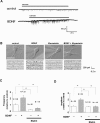
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) exerts multiple biological functions in the CNS. Although BDNF can control transcription and protein synthesis, it still remains open to question whether BDNF regulates lipid biosynthesis. Here we show that BDNF elicits cholesterol biosynthesis in cultured cortical and hippocampal neurons. Importantly, BDNF elicited cholesterol synthesis in neurons, but not in glial cells. Quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR revealed that BDNF stimulated the transcription of enzymes in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. BDNF-induced cholesterol increases were blocked by specific inhibitors of cholesterol synthesis, mevastatin and zaragozic acid, suggesting that BDNF stimulates de novo synthesis of cholesterol rather than the incorporation of extracellular cholesterol. Because cholesterol is a major component of lipid rafts, we investigated whether BDNF would increase the cholesterol content in lipid rafts or nonraft membrane domains. Interestingly, the BDNF-mediated increase in cholesterol occurred in rafts, but not in nonrafts, suggesting that BDNF promotes the development of neuronal lipid rafts. Consistent with this notion, BDNF raised the level of the lipid raft marker protein caveolin-2 in rafts. Remarkably, BDNF increased the levels of presynaptic proteins in lipid rafts, but not in nonrafts. An electrophysiological study revealed that BDNF-dependent cholesterol biosynthesis plays an important role for the development of a readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. Together, these results suggest a novel role for BDNF in cholesterol metabolism and synapse development.
Figures
References
-
- Barres BA, Smith SJ. Neurobiology. Cholesterol—making or breaking the synapse. Science. 2001;294:1296–1297. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom JD, Kurtz MM, Rew DJ, Amend AM, Karkas JD, Bostedor RG, Bansal VS, Dufresne C, VanMiddlesworth FL, Hensens OD, Liesch JM, Zink DL, Wilson KE, Onishi J, Milligan JA, Bills G, Kaplan L, Omstead MN, Jenkins RG, Huang L, et al. Zaragozic acids: a family of fungal metabolites that are picomolar competitive inhibitors of squalene synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:80–84. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bibel M, Barde YA. Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2919–2937. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, Price PJ. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res. 1993;35:567–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
