Effect of behavioral context on representation of a spatial cue in core auditory cortex of awake macaques
- PMID: 17567810
- PMCID: PMC6672434
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0016-07.2007
Effect of behavioral context on representation of a spatial cue in core auditory cortex of awake macaques
Abstract
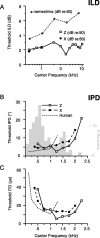
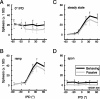
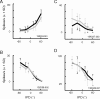
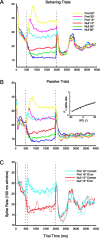
Primary auditory cortex plays a crucial role in spatially directed behavior, but little is known about the effect of behavioral state on the neural representation of spatial cues. Macaques were trained to discriminate binaural cues to sound localization, eventually allowing measurement of thresholds comparable to human hearing. During behavior and passive listening, single units in low-frequency auditory cortex showed robust and consistent tuning to interaural phase difference (IPD). In most neurons, behavior exerted an effect on peak discharge rate (58% increased, 13% decreased), but this was not accompanied by a detectable shift in the best IPD of any cell. Neurometric analysis revealed a difference in discriminability between the behaving and passive condition in half of the sample (52%), but steepening of the neurometric function (29%) was only slightly more common than flattening (23%). This suggests that performance of a discrimination task does not necessarily confer an advantage in understanding the representation of the spatial cue in primary auditory cortex but nevertheless revealed some physiological effects. These results suggest that responses observed during passive listening provide a valid representation of neuronal response properties in core auditory cortex.
Figures





References
-
- Bakin JS, Weinberger NM. Classical conditioning induces CS-specific receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex of the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1990;536:271–286. - PubMed
-
- Benson DA, Hienz RD. Single-unit activity in the auditory cortex of monkeys selectively attending left vs. right ear stimuli. Brain Res. 1978;159:307–320. - PubMed
-
- Benson DA, Hienz RD, Goldstein MH., Jr Single-unit activity in the auditory cortex of monkeys actively localizing sound sources: spatial tuning and behavioral dependency. Brain Res. 1981;219:249–267. - PubMed
-
- Britten KH, Newsome WT, Shadlen MN, Celebrini S, Movshon JA. A relationship between behavioral choice and the visual responses of neurons in macaque MT. Vis Neurosci. 1996;13:87–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
