A novel human ex vivo model for the analysis of molecular events during lung cancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 17567922
- PMCID: PMC1913052
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-43
A novel human ex vivo model for the analysis of molecular events during lung cancer chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) causes most of cancer related deaths in humans and is characterized by poor prognosis regarding efficiency of chemotherapeutical treatment and long-term survival of the patients. The purpose of the present study was the development of a human ex vivo tissue culture model and the analysis of the effects of conventional chemotherapy, which then can serve as a tool to test new chemotherapeutical regimens in NSCLC.
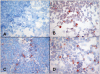
Methods: In a short-term tissue culture model designated STST (Short-Term Stimulation of Tissues) in combination with the novel *HOPE-fixation and paraffin embedding method we examined the responsiveness of 41 human NSCLC tissue specimens to the individual cytotoxic drugs carboplatin, vinorelbine or gemcitabine. Viability was analyzed by LIFE/DEAD assay, TUNEL-staining and colorimetric MTT assay. Expression of Ki-67 protein and of BrdU (bromodeoxyuridine) uptake as markers for proliferation and of cleaved (activated) effector caspase-3 as indicator of late phase apoptosis were assessed by immunohistochemistry. Transcription of caspase-3 was analyzed by RT-PCR. Flow cytometry was utilized to determine caspase-3 in human cancer cell lines.
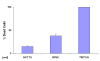
Results: Viability, proliferation and apoptosis of the tissues were moderately affected by cultivation. In human breast cancer, small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and human cell lines (CPC-N, HEK) proliferative capacity was clearly reduced by all 3 chemotherapeutic agents in a very similar manner. Cleavage of caspase-3 was induced in the chemo-sensitive types of cancer (breast cancer, SCLC). Drug-induced effects in human NSCLC tissues were less evident than in the chemo-sensitive tumors with more pronounced effects in adenocarcinomas as compared to squamous cell carcinomas.
Conclusion: Although there was high heterogeneity among the individual tumor tissue responses as expected, we clearly demonstrate specific multiple drug-induced effects simultaneously. Thus, STST provides a useful human model to study numerous aspects of mechanisms underlying tumor responsiveness towards improved anticancer treatment. The results presented here shall serve as a base for multiple functional tests of novel chemotherapeutic approaches to NSCLC in the future.
Figures


References
-
- Cancer Research UK . Statistics and Prognosis for Lung Cancer. Cancer Research UK; 2004.
-
- Goldmann T, Wiedorn KH, Kühl H, Olert J, Branscheid D, Pechkovsky D, Zissel G, Galle J, Müller-Quernheim J, Vollmer E. Assessment of transcriptional gene activity in situ by application of HOPE-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Pathol Res Pract. 2002;198:91–95. doi: 10.1078/0344-0338-00192. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

