Pharmacokinetics of methylprednisolone after intravenous and intramuscular administration in rats
- PMID: 17569107
- PMCID: PMC4181331
- DOI: 10.1002/bdd.551
Pharmacokinetics of methylprednisolone after intravenous and intramuscular administration in rats
Abstract
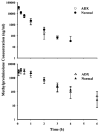
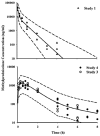
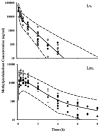
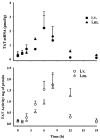
Methylprednisolone (MPL) pharmacokinetics was examined in adrenalectomized (ADX) and normal rats to assess the feasibility of intramuscular (i.m.) dosing for use in pharmacodynamic studies. Several study phases were pursued. Parallel group studies were performed in normal and ADX rats given 50 mg/kg MPL (i.v. or i.m.) and blood samples were collected up to 6 h. Data from studies where normal rats were dosed with 50 mg/kg MPL i.m. and killed over either 6 or 96 h were combined to determine muscle site and plasma MPL concentrations. Lastly, ADX rats were dosed with 50 mg/kg MPL i.m. and killed over 18 h to assess hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT) dynamics. MPL exhibited bi-exponential kinetics after i.v. dosing with a terminal slope of 2.1 h(-1). The i.m. drug was absorbed slowly with two first-order absorption rate constants, 1.26 and 0.219 h(-1) indicating flip-flop kinetics with overall 50% bioavailability. The kinetics of MPL at the injection site exhibited slow, dual absorption rates. Although i.m. MPL showed lower bioavailability compared with other corticosteroids in rats, TAT dynamics revealed similar i.m. and i.v. response profiles. The more convenient intramuscular dosing can replace the i.v. route without causing marked differences in pharmacodynamics.
Figures


References
-
- Belvisi MG, Brown TJ, Wicks S, Foster ML. New glucocorticosteroids with an improved therapeutic ratio? Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2001;14:221–227. - PubMed
-
- Schacke H, Docke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol Ther. 2002;96:23–43. - PubMed
-
- Boudinot FD, D’Ambrosio R, Jusko WJ. Receptor- mediated pharmacodynamics of prednisolone in the rat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1986;14:469–493. - PubMed
-
- Haughey DB, Jusko WJ. Receptor-mediated methylprednisolone pharmacodynamics in rats: steroid-induced receptor down-regulation. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1992;20:333–355. - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishnan R, DuBois DC, Almon RR, Pyszczynski NA, Jusko WJ. Fifth-generation model for corticosteroid pharmacodynamics: application to steady-state receptor down-regulation and enzyme induction patterns during seven-day continuous infusion of methylprednisolone in rats. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2002;29:1–24. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

