Experience with gemcitabine and cisplatin in the therapy of inoperable and metastatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 17569122
- PMCID: PMC4395638
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i20.2852
Experience with gemcitabine and cisplatin in the therapy of inoperable and metastatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: To study the activity of gemcitabine and cisplatin in a cohort of patients with inoperable or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Methods: Chemotherapy-naive patients with pathologically proven cholangiocarcinoma, receiving treatment that consisted of gemcitabine at 1250 mg/m(2) in a 30-min infusion on d 1 and 8, and cisplatin at 75 mg/m(2) at every 21-d cycle, were retrospectively analyzed.
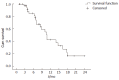
Results: From June 2003 to December 2005, 42 patients were evaluated. Twelve patients (28%) had unresectable disease and 30 (72%) had metastatic disease. There were 28 males and 14 females with a median age of 51 years (range 33-67) and median ECOG PS of 1 (range 0-2). A total of 171 cycles were given with a median number of cycles of 4 (range 1-6). There were 0 CR, 9 PR, 11 SD and 13 PD (response rate 21%). Grade 3-4 hematologic toxicities were: anemia in 33%, neutropenia in 22% and thrombocytopenia in 5%. Non-hematologic toxicity was generally mild. No cases of febrile neutropenia or treatment-related death were noted. The median survival was 10.8 mo (range 8.4-13 mo) and progression free survival was 8.5 mo. One-year survival rate was 40%.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the combination of gemcitabine and cisplatin had consistent efficacy in patients with unresectable or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.
References
-
- Falkson G, MacIntyre JM, Moertel CG. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience with chemotherapy for inoperable gallbladder and bile duct cancer. Cancer. 1984;54:965–969. - PubMed
-
- Takada T, Kato H, Matsushiro T, Nimura Y, Nagakawa T, Nakayama T. Comparison of 5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin and mitomycin C with 5-fluorouracil alone in the treatment of pancreatic-biliary carcinomas. Oncology. 1994;51:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Choi CW, Choi IK, Seo JH, Kim BS, Kim JS, Kim CD, Um SH, Kim JS, Kim YH. Effects of 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in the treatment of pancreatic-biliary tract adenocarcinomas. Am J Clin Oncol. 2000;23:425–428. - PubMed
-
- Kubicka S, Rudolph KL, Tietze MK, Lorenz M, Manns M. Phase II study of systemic gemcitabine chemotherapy for advanced unresectable hepatobiliary carcinomas. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:783–789. - PubMed
-
- Penz M, Kornek GV, Raderer M, Ulrich-Pur H, Fiebiger W, Lenauer A, Depisch D, Krauss G, Schneeweiss B, Scheithauer W. Phase II trial of two-weekly gemcitabine in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer. Ann Oncol. 2001;12:183–186. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials