Synaptopodin protects against proteinuria by disrupting Cdc42:IRSp53:Mena signaling complexes in kidney podocytes
- PMID: 17569780
- PMCID: PMC1934530
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070075
Synaptopodin protects against proteinuria by disrupting Cdc42:IRSp53:Mena signaling complexes in kidney podocytes
Abstract
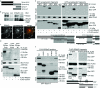
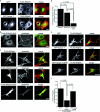
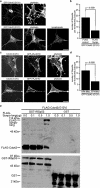
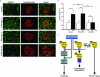
The actin-based foot processes of kidney podocytes and the interposed slit diaphragm form the final barrier to proteinuria. Mutations affecting several podocyte proteins cause disruption of the filtration barrier and rearrangement of the highly dynamic podocyte actin cytoskeleton. Proteins regulating the plasticity of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton are therefore of critical importance for sustained kidney barrier function. Synaptopodin is an actin-associated protein essential for the integrity of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton because synaptopodin-deficient mice display impaired recovery from protamine sulfate-induced foot process effacement and lipopolysaccharide-induced nephrotic syndrome. Moreover, bigenic heterozygosity for synaptopodin and CD2AP is sufficient to induce spontaneous proteinuria and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis-like glomerular damage in mice. Mechanistically, synaptopodin induces stress fibers by blocking the proteasomal degradation of RhoA. Here we show that synaptopodin directly binds to IRSp53 and suppresses Cdc42:IRSp53:Mena-initiated filopodia formation by blocking the binding of Cdc42 and Mena to IRSp53. The Mena inhibitor FP(4)-Mito suppresses aberrant filopodia formation in synaptopodin knockdown podocytes, and when delivered into mice protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced proteinuria. The identification of synaptopodin as an inhibitor of Cdc42:IRSp53:Mena signaling defines a novel antiproteinuric signaling pathway and offers new targets for the development of antiproteinuric therapeutic modalities.
Figures


References
-
- Mundel P, Kriz W. Structure and function of podocytes: an update. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1995;192:385–397. - PubMed
-
- Somlo S, Mundel P. Getting a foothold in nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet. 2000;24:333–335. - PubMed
-
- Drenckhahn D, Franke RP. Ultrastructural organization of contractile and cytoskeletal proteins in glomerular podocytes of chicken, rat, and man. Lab Invest. 1988;59:673–682. - PubMed
-
- Oh J, Reiser J, Mundel P. Dynamic (re)organization of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton in the nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2004;19:130–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

