An enhancer-like region regulates hrp3 promoter stage-specific gene expression in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 17570541
- PMCID: PMC2267920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.04.009
An enhancer-like region regulates hrp3 promoter stage-specific gene expression in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
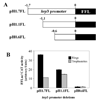
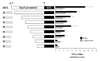
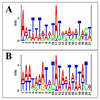
The asexual blood stage of Plasmodium falciparum is comprised of morphologically distinct ring, trophozoite and schizont stages. Each of these developmental stages possesses a distinct pattern of gene expression. Regulation of P. falciparum gene expression is thought to occur, at least in part, at the promoter level. Previously, we have found that although the hrp3 mRNA is only seen in ring-stage parasites, deletion of a specific sequence in the 5' end of the promoter region decreased ring-stage expression of hrp3 and enabled detection of its transcripts in trophozoite-stage parasites. In order to investigate this stage specific regulation of gene expression, we employed a series of nested deletions of the 1.7-kb hrp3 promoter. Firefly luciferase gene was used as a reporter to evaluate the role of promoter sequences in gene regulation. Using this approach, we identified a ring-stage specific regulatory region on the hrp3 promoter located between -1.7 kb and -1.1 kb from the ATG initiation codon. Small 100-150 bp truncations on this enhancer-like region failed to uncover discrete regulatory sequences, suggesting the multipartite nature of this element. The data presented in this study demonstrate that stage specific promoter activity of the hrp3 gene in P. falciparum blood stage parasites is supported, at least in-part, by a small promoter region that can function in the absence of a larger chromosomal context.
Figures


References
-
- Global. WHO declares emergency against AIDS, TB, malaria. AIDS policy & law. 2006;21:5. - PubMed
-
- Simooya O. The WHO 'Roll Back Malaria Project': planning for adverse event monitoring in Africa. Drug Saf. 2005;28:277–286. - PubMed
-
- Wesseling JG, Snijders PJ, van Someren P, Jansen J, Smits MA, Schoenmakers JG. Stage-specific expression and genomic organization of the actin genes of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989;35:167–176. - PubMed
-
- Waters AP, Syin C, McCutchan TF. Developmental regulation of stage-specific ribosome populations in Plasmodium. Nature. 1989;342:438–440. - PubMed
-
- Waters AP. The ribosomal RNA genes of Plasmodium. Adv Parasitol. 1994;34:33–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

