Genomorama: genome visualization and analysis
- PMID: 17570856
- PMCID: PMC1906841
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-204
Genomorama: genome visualization and analysis
Abstract
Background: The ability to visualize genomic features and design experimental assays that can target specific regions of a genome is essential for modern biology. To assist in these tasks, we present Genomorama, a software program for interactively displaying multiple genomes and identifying potential DNA hybridization sites for assay design.
Results: Useful features of Genomorama include genome search by DNA hybridization (probe binding and PCR amplification), efficient multi-scale display and manipulation of multiple genomes, support for many genome file types and the ability to search for and retrieve data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Entrez server.
Conclusion: Genomorama provides an efficient computational platform for visualizing and analyzing multiple genomes.
Figures
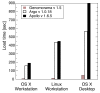

Similar articles
-
COMPAM :visualization of combining pairwise alignments for multiple genomes.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jan 15;22(2):242-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti759. Epub 2005 Nov 3. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16269416
-
Combo: a whole genome comparative browser.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jul 15;22(14):1782-3. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl193. Epub 2006 May 18. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16709588
-
PSAT: a web tool to compare genomic neighborhoods of multiple prokaryotic genomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Mar 26;9:170. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-170. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18366802 Free PMC article.
-
Computational and bioinformatics frameworks for next-generation whole exome and genome sequencing.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;2013:730210. doi: 10.1155/2013/730210. Epub 2013 Jan 13. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 23365548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automated querying of genome databases.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jan 26;3(1):e1. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030001. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17257048 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
JCoast - a biologist-centric software tool for data mining and comparison of prokaryotic (meta)genomes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Apr 1;9:177. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-177. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18380896 Free PMC article.
-
BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons.BMC Genomics. 2011 Aug 8;12:402. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-402. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21824423 Free PMC article.
-
CompaGB: An open framework for genome browsers comparison.BMC Res Notes. 2011 May 4;4:133. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-133. BMC Res Notes. 2011. PMID: 21542900 Free PMC article.
-
3D genome tuner: compare multiple circular genomes in a 3D context.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2009 Sep;7(3):143-6. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(08)60043-1. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19944387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lewis SE, Searle SMJ, Harris N, Gibson M, Iyer V, Richter J, Wiel C, Bayraktaroglu L, Birney E, Crosby MA, Kaminker JS, Matthews BB, Prochnik SE, Smithy CD, Tupy JL, Rubin GM, Misra S, Mungall CJ, Clamp ME. Apollo: a sequence annotation editor. Genome Biology. 2002;3:1–14. doi: 10.1186/gb-2002-3-12-research0082. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turinsky AL, Ah-Seng AC, Gordon PMK, Stromer JN, Taschuk ML, Xu EW, Sensen CW. Bioinformatics visualization and integration with open standards: The Bluejay genomic browser. In Silico Biology. 2004;5 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

