Silver nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates based on DNA with triple cyclic disulfide moieties
- PMID: 17571909
- PMCID: PMC3200546
- DOI: 10.1021/nl071108g
Silver nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates based on DNA with triple cyclic disulfide moieties
Abstract
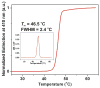
We report a new strategy for preparing silver nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates that are based upon DNA with cyclic disulfide-anchoring groups. These particles are extremely stable and can withstand NaCl concentrations up to 1.0 M. When silver nanoparticles functionalized with complementary sequences are combined, they assemble to form DNA-linked nanoparticle networks. This assembly process is reversible with heating and is associated with a red shifting of the particle surface plasmon resonance and a concomitant color change from yellow to pale red. Analogous to the oligonucleotide-functionalized gold nanoparticles, these particles also exhibit highly cooperative binding properties with extremely sharp melting transitions. This work is an important step toward using silver nanoparticle-oligonucleotide conjugates for a variety of purposes, including molecular diagnostic labels, synthons in programmable materials synthesis approaches, and functional components for nanoelectronic and plasmonic devices.
Figures


References
-
- Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Mucic RC, Storhoff JJ. Nature. 1996;382:607–609. - PubMed
-
- Alivisatos AP, Johnsson KP, Peng X, Wilson TE, Loweth CJ, Bruchez MP, Schultz PG. Nature. 1996;382:609–611. - PubMed
-
- Storhoff JJ, Lazarides AA, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL, Scatz GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:4640–4650.
-
- Jin R, Wu G, Li Z, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:1643–1654. - PubMed
-
- Lytton-Jean AKR, Mirkin CA. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:12754–12755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

