High-resolution chest CT findings do not predict the presence of pulmonary hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 17573485
- PMCID: PMC2093962
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.07-0116
High-resolution chest CT findings do not predict the presence of pulmonary hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Reliable, noninvasive approaches to the diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) are needed. We tested the hypothesis that chest CT-determined extent of pulmonary fibrosis and/or main pulmonary artery diameter (MPAD) can be used to identify the presence of PH in patients with advanced IPF.
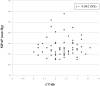
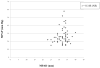
Methods: Cross-sectional study of 65 patients with advanced IPF and available right-heart catheterization and high-resolution chest CT. An expert radiologist scored ground-glass opacity, lung fibrosis, and honeycombing in the CT images on a scale of 0 to 4. These scores were also summed into a total profusion score. The main pulmonary artery was measured at its widest dimension on the supine full-chest sequence. At this same level, the widest aorta diameter was measured.
Results: Chest CT-determined fibrosis score, ground-glass opacity score, honeycombing score, total profusion score, diameter of the main pulmonary artery, and the ratio of the pulmonary artery to aorta diameter did not differ between those with and without PH. There was no significant correlation between mean pulmonary artery pressure and any of the chest CT-determined measures.
Conclusions: High-resolution chest CT-determined extent of pulmonary fibrosis and/or MPAD cannot be used to screen for PH in advanced IPF patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Utility of CT for predicting pulmonary hypertension in patients with parenchymal lung disease: similar results, different conclusion?Chest. 2008 Apr;133(4):1053-4; author reply 1054. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-2761. Chest. 2008. PMID: 18398135 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
-
- Lettieri CJ, Nathan SD, Barnett SD, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of pulmonary arterial hypertension in advanced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2006;129:746–752. - PubMed
-
- Nadrous HF, Pellikka PA, Krowka MJ, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2005;128:2393–2399. - PubMed
-
- Weitzenblum E, Ehrhart M, Rasaholinjanahary J, et al. Pulmonary hemodynamics in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial pulmonary diseases. Respiration. 1983;44:118–127. - PubMed

