A specialized nucleosome has a "point" to make
- PMID: 17574019
- PMCID: PMC2950099
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.05.054
A specialized nucleosome has a "point" to make
Abstract
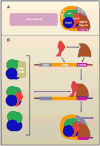
Three recent papers, including Mizuguchi et al. (2007) in this issue, show that the nonhistone protein Scm3 is required for the recruitment of the histone H3 variant Cse4 to centromeres in budding yeast. Scm3 forms a chromatin component with Cse4:histone H4 tetramers that appear to lack H2A/H2B histones. These studies provide key insights into the pathway that recruits Cse4 to centromeres and have important implications for other functions of chromatin.
Figures
Comment on
-
Nonhistone Scm3 and histones CenH3-H4 assemble the core of centromere-specific nucleosomes.Cell. 2007 Jun 15;129(6):1153-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.026. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17574026
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

